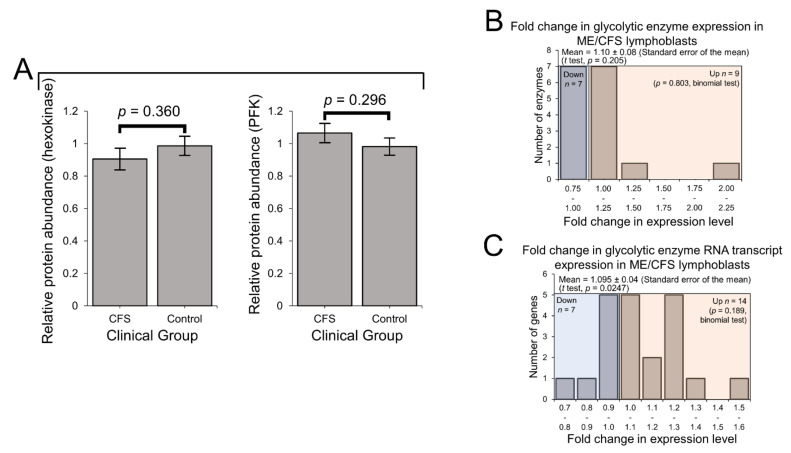
Figure 3.
Protein-level expression of glycolytic enzymes is unchanged in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) lymphoblasts. Error bars represent the standard errors of the mean. RNA sequencing transcriptomics experiment: ME/CFS n = 23, control n = 17. Each cell line was sampled once. Mass spectrometry proteomics experiment: ME/CFS n = 34, control n = 31. Each cell line was sampled once, or twice for a subset of healthy controls arbitrarily selected to act as an internal control between experiments in the proteomics work. (A) The expression level of hexokinase and phosphofructokinase is unchanged in whole-cell mass spectrometry proteomics experiments (independent t test). Relative hexokinase (HK) and phosphofructokinase (PFK) abundance was calculated by averaging the mean fold change in the ME/CFS group for each isoenzyme/subunit of the respective enzyme (none of which were statistically significant on their own, threshold p < 0.05). (B) A total of 16 glycolytic enzymes were detected within the whole-cell proteomes of lymphoblasts from ME/CFS and control lymphoblasts. Fold change refers to the mean abundance of a given protein in the CFS group divided by the mean abundance in the control group. There was no significant difference in the differentially expressed proportions of detected glycolytic enzymes (binomial test with Ho set to 0.5) or the magnitude of expression (single-sample t test with Ho m = 1) between ME/CFS and controls. (C) A total of 21 RNA transcripts encoding glycolytic enzymes were detected by RNA sequencing within the whole-cell transcriptomes of ME/CFS and control lymphoblasts. Mean fold change was calculated for the ME/CFS group versus the control average for each transcript. The proportion of detected transcripts that were upregulated (binomial test with Ho set to 0.5) was not significant while the average extent of the upregulation (single-sample t test with Ho m = 1) was statistically significant.