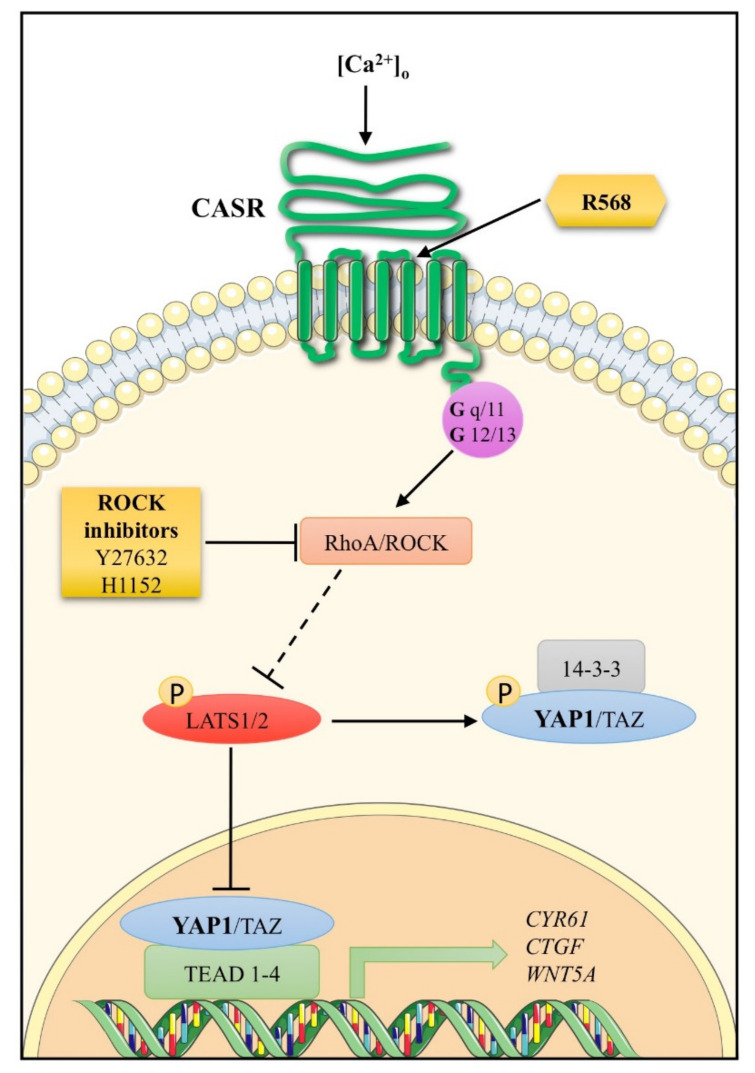
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of the CASR-ROCK-YAP1 signaling pathway in tumor parathyroid cells. Stimulation of the calcium-sensing receptor with Ca2+ or R568 through the coupling with Gα12/13 or Gαq/11 leads to activation of small GTPase protein RhoA, which indirectly inhibits LATS kinase activity. LATS1/2 phosphorylates YAP1 on highly conserved residues of serine. The phosphorylation of YAP1 promotes cytoplasmic retention and degradation. However, when RhoA inhibits LATS1/2, dephosphorylated YAP1 translocates into the nucleus, where it binds and activates TEAD transcription factors, inducing the expression of multiple genes. Part of this figure was created with images from Servier Medical Art (http://smart.servier.com/, accessed on 1 January 2021), licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/, accessed on 1 January 2021).