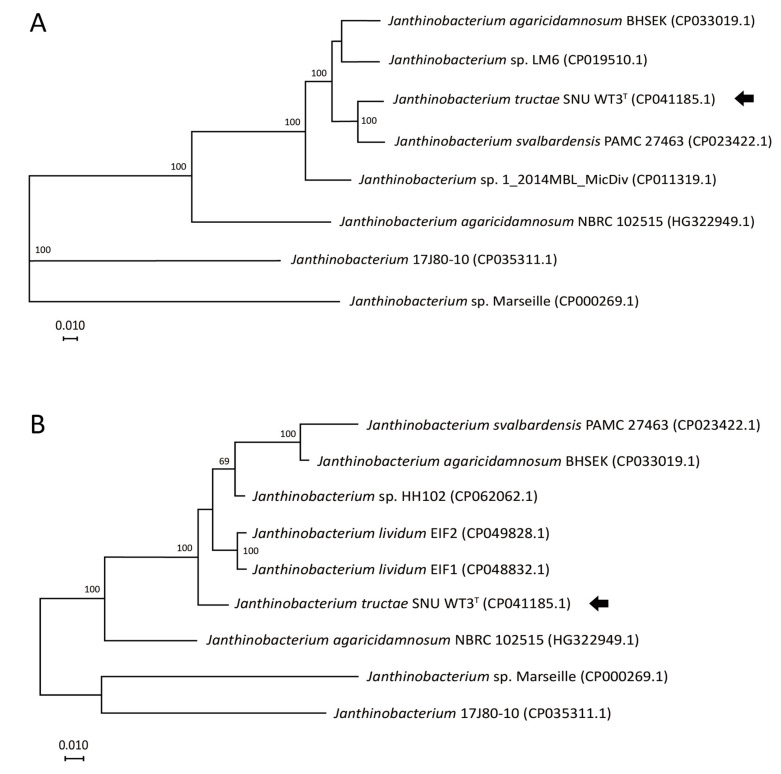
Figure 6.
Core genome phylogeny and multilocus sequence alignment (MLSA) tree of Janthinobacterium species. (A) Core genome phylogenetic tree was constructed using EDGAR 2.0 [25]. Core gene sets were aligned using MUSCLE and concatenated. An approximately maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree was constructed with FastTree. Local support values were shown next to the branches as percentages. (B) An unrooted tree was constructed from four concatenated housekeeping genes extracted from the complete genome sequences of nine Janthinobacterium strains. The tree was inferred using the maximum-likelihood method and the Tamura and Nei (1993) model with MEGA X and was drawn to scale [19,20]. The maximum composite likelihood method was used to calculate evolutionary distances [21]. Missing data or gaps were completely deleted, and the phylogeny was evaluated using 1000 bootstrap replicates. The percentage values of associated taxa clustered together are indicated next to the branches. Scale bars = 0.010 changes per nucleotide position. Strain SNU WT3 is indicated with an arrow.