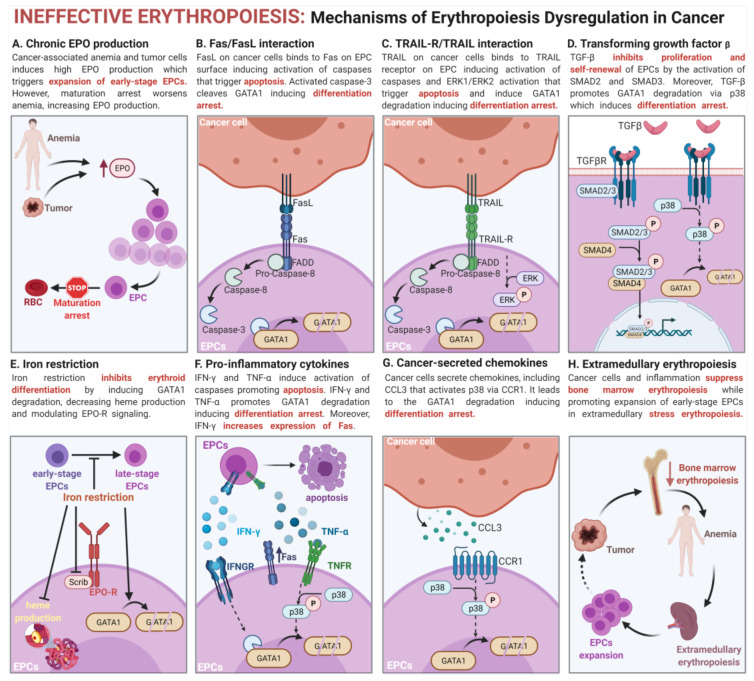
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of erythropoiesis dysregulation in cancer. Expansion of early-stage EPCs is caused by (A) chronic erythropoietin (EPO) production. However, EPCs are unable to generate mature red blood cells (RBCs) due to increased apoptosis and differentiation arrest. EPCs apoptosis is triggered by (B) FasL/Fas and (C) TRAIL-TRAIL-R interaction between EPCs and cancer cells. Differentiation arrest of early-stage EPCs is caused by (D) transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), (E) iron restriction, (F) pro-inflammatory cytokines, and (G) cancer-secreted chemokines. Inhibited maturation is an effect of GATA1 degradation mediated by caspase-3 or p38 activation. (H) Bone marrow steady-state erythropoiesis is suppressed by inflammation and triggers stress erythropoiesis and expansion of EPCs in extramedullary sites.