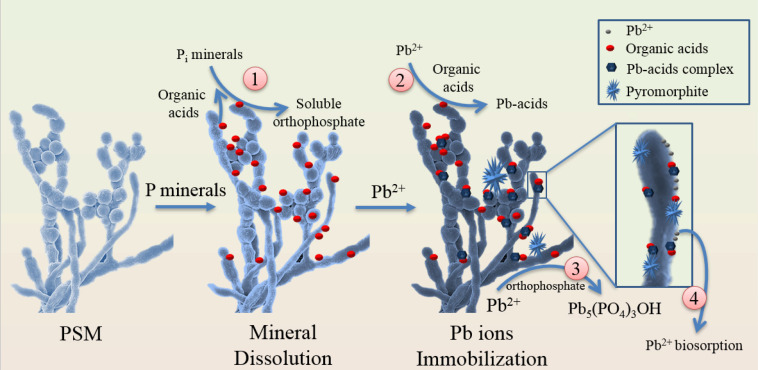
Figure 3.
Simplified representation of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms (PSM)-induced dissolution to accelerate lead (Pb) precipitation to form secondary inorganic P (Pi) minerals. ① PSM can dissolve Pi minerals to soluble orthophosphate by releasing organic acids. ② Pb ions in the solution are precipitated to Pb–acid complexes by reacting with organic acids that are released by PSM. ③ In the presence of orthophosphate (H2PO4–, HPO42–), Pb ions are precipitated to the relatively stable pyromorphite. ④ Pb ions in the solution are biosorbed to PSM surface due to the negative charges of the surface functional groups.