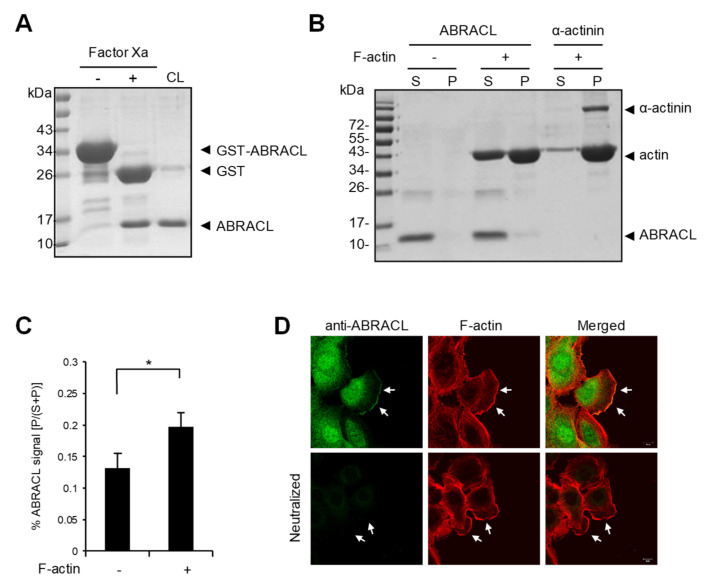
Figure 4.
ABRACL associates with the actin cytoskeleton. (A) Preparation of recombinant ABRACL. GST-ABRACL purified from E. coli was treated with Factor Xa and subjected to clean-up steps to obtain ABRACL. Shown is a gel image after Coomassie blue staining. CL, cleaned-up sample. (B) In vitro F-actin sedimentation assay. Non-muscle actin (Cytoskeleton, Inc., Denver, CO, USA) was polymerized into F-actin and incubated with purified ABRACL or α-actinin (Cytoskeleton, Inc., Denver, CO, USA) as a control. After centrifugation to sediment F-actin, supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and Coomassie Blue staining. (C) Quantitative results of ABRACL co-sedimentation with F-actin. Quantitation of ABRACL signal was done by MultiGauge software. The P/(S+P) signal ratios were calculated. Shown are Mean ± SD from independent experiments shown in (B) and Figure S2. (D) Colocalization of ABRACL and F-actin. Monolayers of MDA-MB-231 cells were fixed after a scratch “wound” was made and subjected to ABRACL immunofluorescence staining and F-actin staining (using TRITC-phalloidin). In the neutralized control sample, purified ABRACL was added during immunofluorescence staining to neutralize the antibodies. Shown are confocal micrographs. Arrows, lamellipodia.