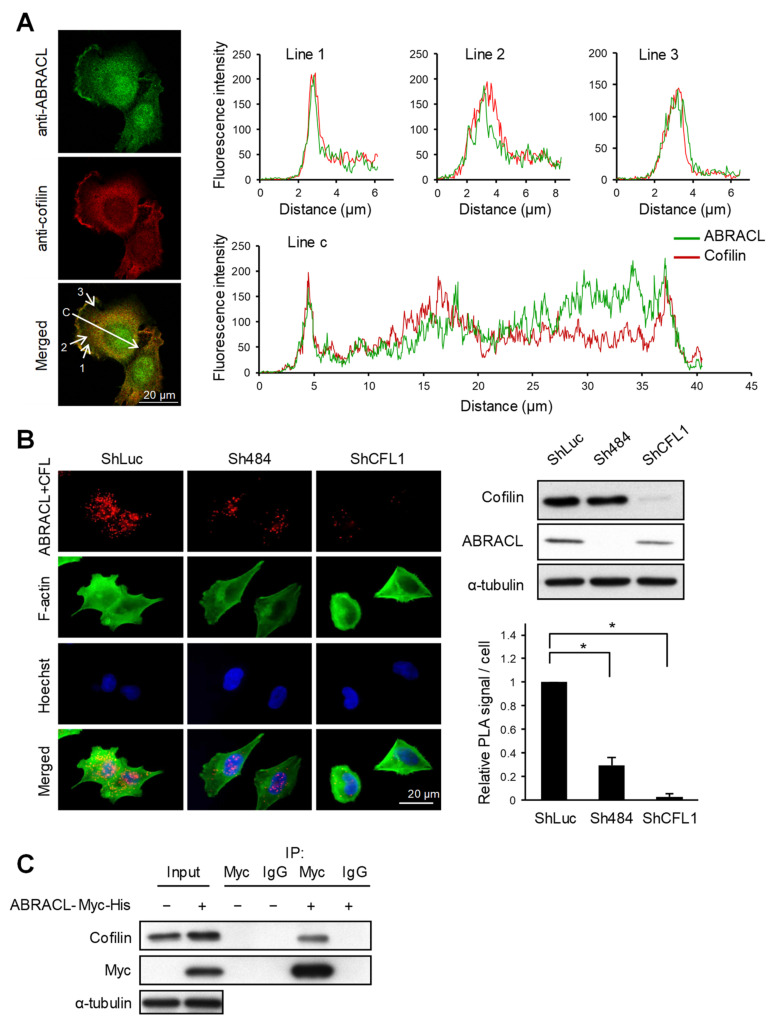
Figure 6.
ABRACL interacts with cofilin. (A) Immunofluorescence staining. MDA-MB-231 cells were fixed and incubated with both anti-ABRACL and anti-cofilin primary antibodies in the procedure. Fluorescence signals were captured under a confocal microscope. Colocalization of ABRACL and cofilin signals along the shown lines (1, 2, 3, and c) were quantified and plotted against the distance from the origin of each line. (B) In situ proximity ligation assay (PLA). HCT116 cells infected with luciferase-targeting (shLuc), ABRACL-targeting (Sh484) or cofilin-targeting (shCFL1-1) shRNA-expressing lentivirus were analyzed. Cells were fixed, incubated with anti-ABRACL and anti-cofilin antibodies, and subjected to in situ PLA using the Duolink kit (Sigma-Aldrich). Cells were also stained with FITC-phalloidin for F-actin and Hoechst for DNA. Representative fluorescence micrographs and Western analysis confirming the knockdown effects are shown. Fluorescence signals from PLA were quantitated by counting the signal spots in each cell. Signal intensities relative to the shLuc control sample are shown. *, p < 0.01. (C) Co-immunoprecipitation assay. Lysates prepared from cells transfected with the control vector (−) or pcDNA3.1Myc/His-ABRACL (+) were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-Myc antibodies or IgG (as a negative control). Immunoprecipitated proteins were subjected to SDS–PAGE and Western analysis.