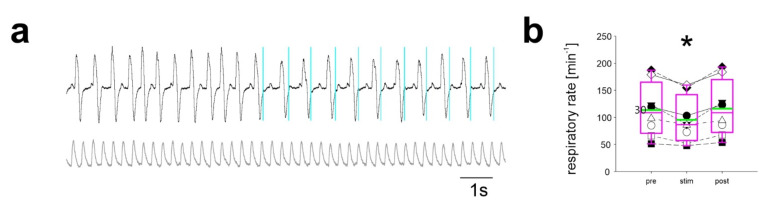
Figure 4.
Stimulation during expiration leads to reduction in respiratory rate. (a) Breathing recorded with the piezo-sensor (gray trace: pulse signal measured by pulse oximetry). Stimulation with a 20 ms light pulse (blue bars) during expiration leads to an increase of the interval and, thus, (b) A reduction in the respiratory rate (* p < 0.001; One Way RM ANOVA; n = 8 mice).