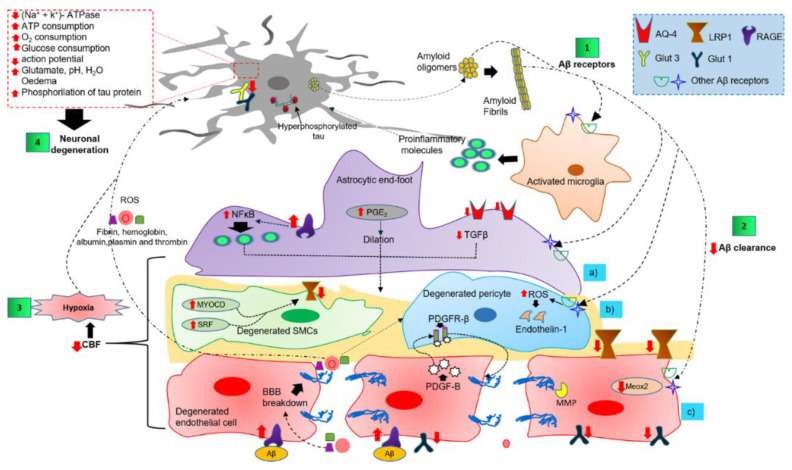
Figure 3.
Overview of the complex cell–cell signaling in the NVU, triggered by extracellular and vascular Aβ deposits. Step 1 shows the interaction of Aβ oligomers and fibrils with NVU cells through several receptors. Step 2 illustrates the altered Aβ clearance that triggers NVU dysfunction. Step 3 shows the NVU cell dysfunction as the causative agent of cerebral hypoxia. Step 4 shows cerebral hypoxia, neuroinflammatory environment, and peripheral blood infiltrate as the promoting causes of neuronal degeneration. Abbreviations: AQ-4, aquaporin-4; Aβ, amyloid peptide; BBB, blood-brain barrier; CBF, cerebral blood flow; GLUT, glucose transporter; LRP1, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1; MEOX2, mesenchyme homeobox 2; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MYOCD, myocardin; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells; PDGF-B, platelet-derived growth factor subunit B; PDGFRβ, platelet-derived growth factor receptor β; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; TGFβ, transforming growth factor-beta; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation end products; ROS, reactive oxygen species.