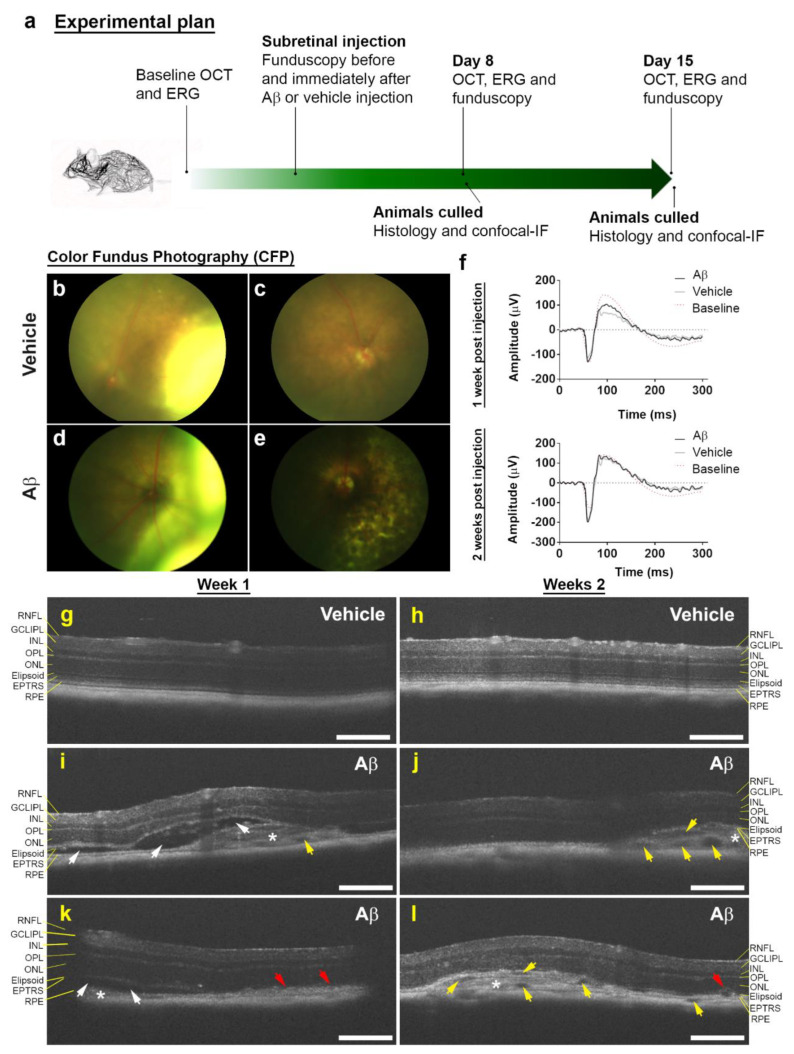
Figure 1.
Subretinal Aβ effects in retinas of living mouse eyes. (a) Schematic plan showing experimental sequence. (b) Representative color fundus photograph (CFP) of mouse eye injected with vehicle immediately after and (c) 8 days following subretinal injection. Note, the appearance of a retinal bleb following a successful transscleral subretinal injection, which subsequently resolves. (d) Representative CFP of mouse eye injected with human oligomeric Aβ1-42 immediately after and (e) 8 days later. Note superficial evidence of retinal pathology following exposure to Aβ. (f) Average scotopic ERG responses in mice injected with vehicle (n = 6) or human oligomeric Aβ1-42 (n = 7) after 1 and 2 weeks. No significant differences in retinal function were observed between eyes injected with Aβ vs. controls by Mann–Whitney U test (two tailed). (g) Representative optical coherence tomography (OCT) images of vehicle and (i,k) human oligomeric Aβ1-42-injected eyes after 1 week. We observed areas of localized pathology in eyes exposed Aβ1-42 consisting of RPE disruption (red arrows), subretinal fluid accumulation (white arrows) and hyper-reflective material (asterisk). There was also evidence of occasional hypo-reflective spaces (yellow arrows). However, by week 2, subretinal fluid accumulation appeared to have been largely resolved (j,l), but there was increasing evidence of hypo-reflective spaces. We also observed disrupted RPE and subretinal hyper-reflective material persisting in week 2. There was no evidence of pathogenic features in eyes injected with vehicle at either 1 or 2 weeks (g,h). Scale bars correspond to 200 μm.