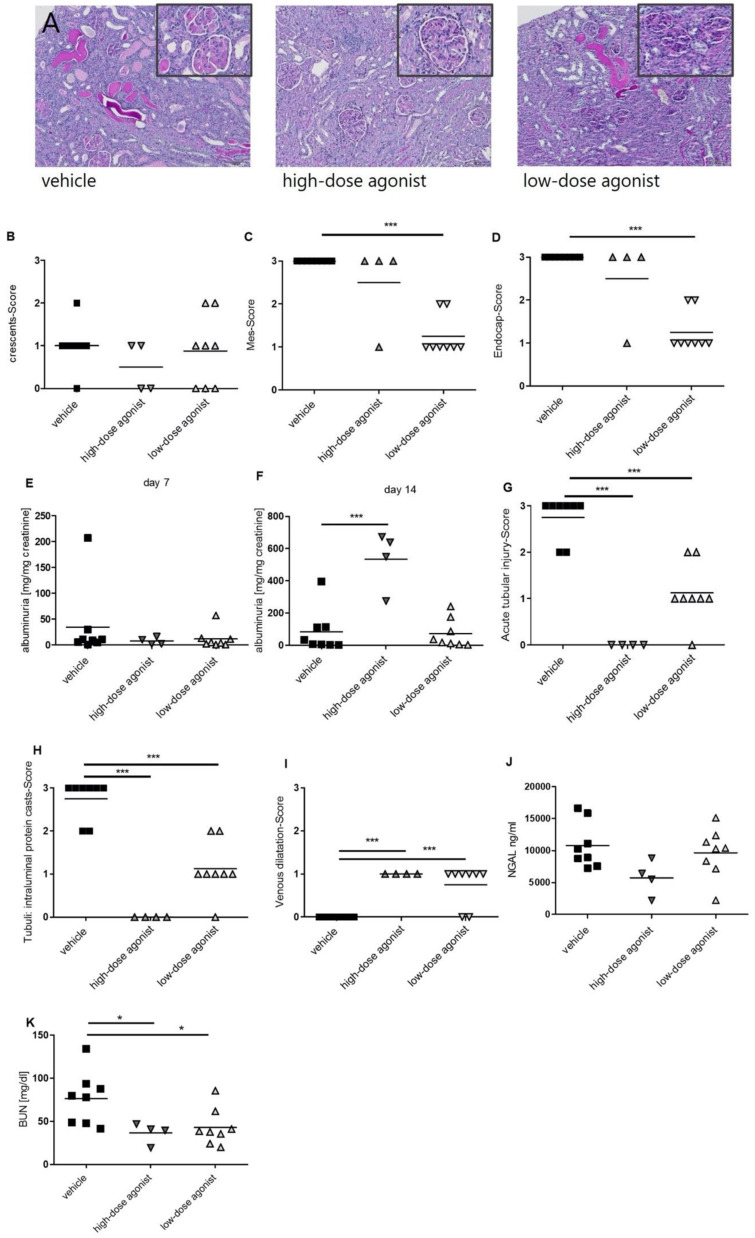
Figure 1.
EP4 receptor agonism improved the phenotype of nephrotoxic serum nephritis (NTS). Fourteen days after NTS induction, kidneys of mice treated with vehicle, high-dose EP4 receptor agonist, or low-dose EP4 receptor agonist were harvested, and PAS-staining was performed (A). Representative pictures are shown. Stained kidney sections were quantified for glomerular and kidney damage (B–D). Urine samples collected on day 7 (E) and 14 (F) were analyzed for albumin and creatinine. In order to quantify for tubular damage acute tubular injury score (G) and tubular cast formation, six high-power fields (HPF) (H) were evaluated. Venous dilatation score (I) was quantified. Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) levels (J) and serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels (K) were evaluated on day 14. (* p ≤ 0.05, *** p ≤ 0.001).