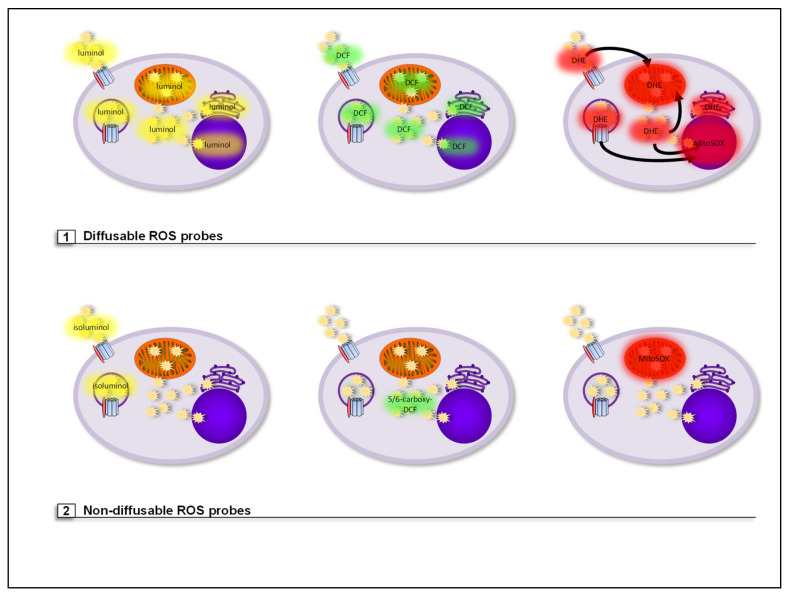
Figure 7.
(1) Diffusible ROS probes are not retained or targeted to a specific cellular compartment. Luminol is a luminophore that reacts with all types of ROS. Luminol-based chemiluminescence represents a quantitative value for the amount of ROS generated but since this probe is diffusible, both extra- and intracellular ROS, i.e., total cellular ROS, are detected. H2DCF-DA is a cell-permeable derivative of fluorescein and one of the most commonly used ROS probes. H2DCF-DA is often referred to as intracellular ROS probe. However, it is diffusible and therefore does not only remain in the cytosol but also reaches cell organelles and diffuses back into the extracellular space. Therefore, like with luminol, only total cellular ROS can be detected with this probe. DHE is a red fluorescent probe that rather specifically reacts with cellular O2●− resulting in red fluorescence. However, it easily crosses cellular membranes and therefore can be oxidized by O2●− anywhere in and outside of the cell. Therefore, with this probe only total cellular O2●− production can be detected. Oxidation of DHE generates two products, 2-hydroxyethidium and ethidium. Both products bind to DNA, which highly increase their fluorescence. This may lead to false interpretations regarding the localization of ROS production, namely DNA containing organelles such as the nucleus and mitochondria, when fluorescence microscopy is used to analyze ROS production. (2) Some ROS probes are either cell-impermeable, targeted to or retained in a specific cellular compartment. Isoluminol is a cell-impermeable derivative of luminol. This makes it ideal for exclusive measurement of extracellular ROS, which also includes ROS produced into the lumen of endosomes and phagosomes. 5/6-Carboxy-DCF is a derivative of H2DCF-DA that contains two additional carboxyl groups that enhance its hydrophilicity and therefore strongly increase its retention in the cytosol. Therefore, 5/6-Carboxy-DCF can be used to specifically detect cytosolic ROS levels. MitoSOX is accumulated in the mitochondrial matrix and specifically detects O2●−.