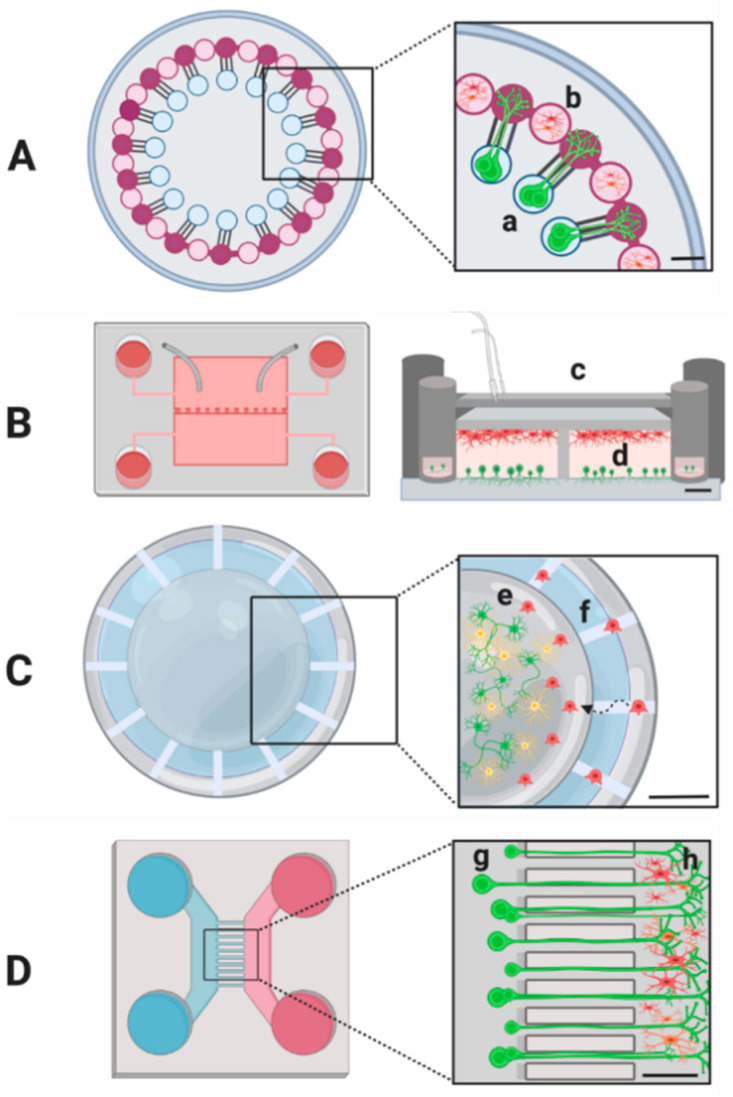
Figure 2.
Schematics showing examples of microfluidic platforms from the literature. Microglia (red), neurons (green) and astrocytes (yellow). (A) Circular compartmentalized platform with multiple independent units consisting of somal (a) and axonal compartments. Microglia is placed in spatially defined areas (b) arrayed between bundles of axons outgrowth; scale bar, 500 µm [206]. (B) Vertically layered configuration with four mirror image cylinders as media reservoirs with a pressure chamber to control neuron–glia interactions. Cross-section (c) showing attached glia on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) roof of culture chamber and neurons attached to platform glass surface; scale bar, 200 µm (d) [208]. (C) 3D tri-culture system consisting of a central matrigel-coated chamber with 3D neurons/astrocytes (e) and microglia in angular chambers (f). Scale bar, 500 µm [191]. (D) Microfluidic platform to establish directional growth and isolation of axons. Microchannels separating somal (g) and axonal (h) compartments. Scale bar, 250 µm [209].