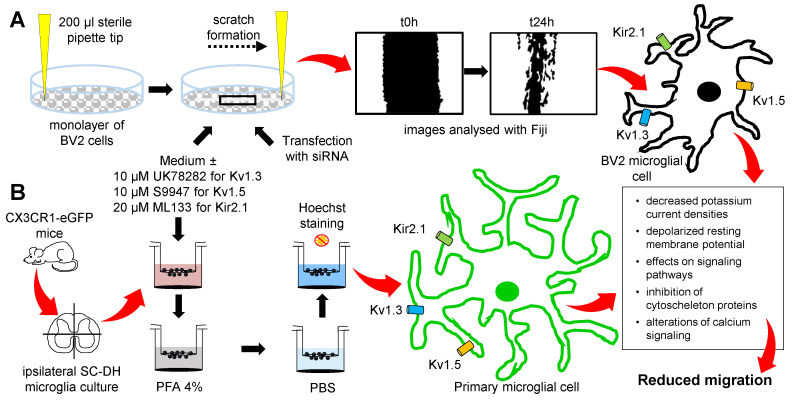
Figure 6.
The experimental steps showing the inhibitory effect of potassium channels on microglial migration. (A) The monolayer of BV2 microglial cells was scratched with a sterile pipette tip and incubated with the medium or the pharmacological inhibitors or the cells were transfected with small interfering RNA (siRNA); pictures were analyzed at t24h and the inhibition of Kv1.3 and Kir2.1 reduced the rate of migration in the BV2 microglial cell line. (B) CX3CR1-eGFP transgenic mice were subjected to SNI or sham surgeries, the ipsilateral spinal cord dorsal horn (SC-DH) was dissected and cultured for 3 h in 8 µm pore inserts, in the culture medium or in the presence of the inhibitors, and the rate of migration was quantified in each condition. Different mechanisms by which the inhibition of the investigated potassium channels may influence the microglial migration rate, are proposed in the outlined box. PBS: phosphate buffer saline; PFA: paraformaldehyde.