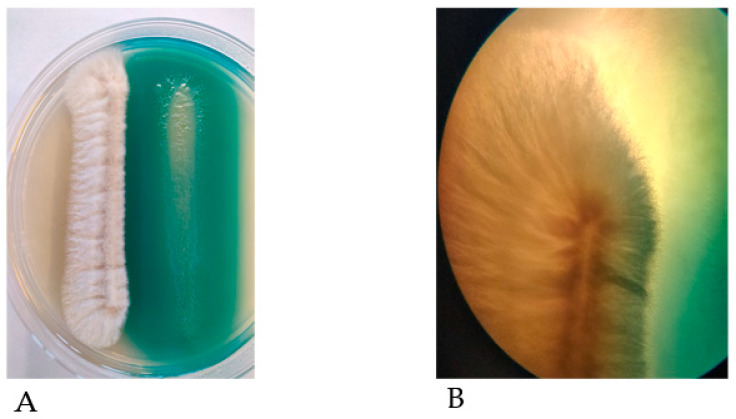
Figure 1.
(A) P. aeruginosa cells (right) grown alongside A. fumigatus conidia (left) on nutrient agar. P. aeruginosa inhibits growth of A. fumigatus as evidenced by reduced mycelial expansion on the side of bacterial growth. The green pigment produced by P. aeruginosa is pyocyanin. (B) A magnified image of (A) in which A. fumigatus growth is inhibited by P. aeruginosa; the expansion of A. fumigatus mycelia are inhibited by the close proximity to P. aeruginosa cells. By contrast, the absence of bacteria on the left hand side of the fungus allow mycelia to expand outward.