Fig. 5 |. Structural features of the peptide, UDP and lectin-domain GalNAc-binding sites of TgGalNAc-T3.
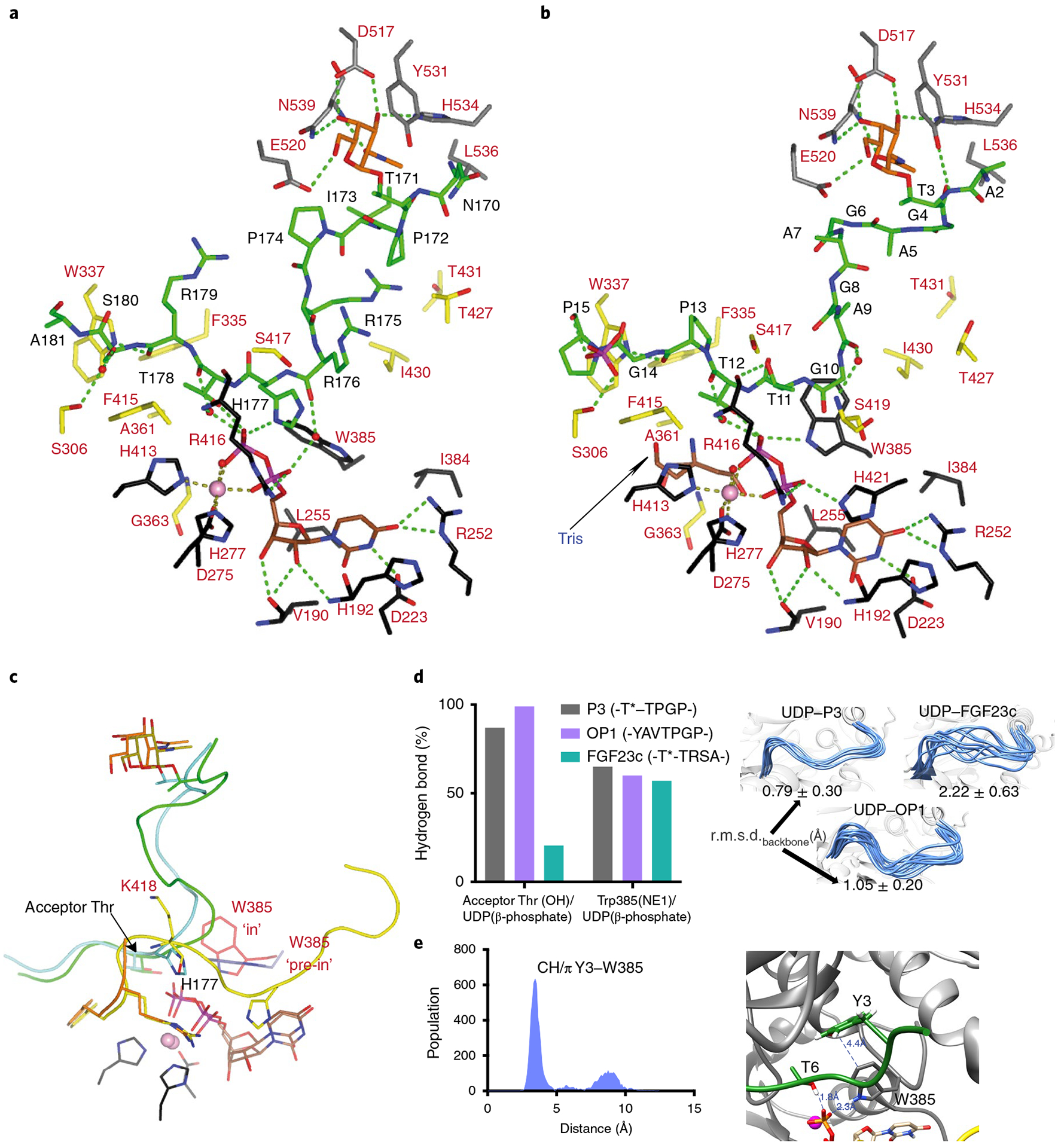
a,b, View of the complete sugar-nucleotide, peptide and lectin-domain binding sites of TgGalNAc-T3–UDP–FGF23c (a) and TgGalNAc-T3–UDP–P3 (b) complexes. Residues forming the sugar-nucleotide, peptide and lectin-domain binding sites are depicted as black, yellow and gray carbon atoms, respectively. UDP and the glycopeptide are shown as brown and green carbon atoms, respectively. Mn2+ and GalNAc moiety are depicted as a pink sphere and orange carbon atoms, respectively. Hydrogen bond interactions are shown as dotted green lines. Water molecules are depicted as red spheres. Note that only water-mediated interactions in which only one water molecule acts as a bridge between the residues are shown. In the TgGalNAc-T3–UDP–FGF23c complex, a phosphate and a Tris molecule are identified in the catalytic domain active site. c, Close-up view of the superimposed TgGalNAc-T3–UDP–P3 (flexible loop in yellow) and TgGalNAc-T3–UDP–FGF23c (flexible loop in orange) complexes. Amino acid residues of P3 and FGF23c are colored green and aquamarine, respectively, while their GalNAc moieties are colored olive and orange, respectively. Trp385 in either the in or pre-in conformation is colored as red and black carbon atoms, respectively. d, Extent of hydrogen bond formation between the acceptor Thr OH and UDP phosphate and Trp385 and UDP phosphate obtained from 0.5 μs MD simulations of TgGalNAc-T3–UDP–P3, TgGalNAc-T3–UDP–FGF23c and TgGalNAc-T3–UDP–OP1. Note that for the MD simulations of TgGalNAc-T3–UDP–FGF23c we used the FGF23c without the EDDS sequence as no electron density for the EDDS sequence was visualized in the crystal structure (left). Ensemble of structures obtained from the MD simulations showing differences in the stability of the flexible loop for the closed conformation (right). e, Analysis of the CH–π interaction between the optimal OP1 Tyr3 and GalNAc-T3 Trp385 obtained by MD simulations (left). Close-up view of the CH–π interaction between Tyr3 and Trp385 (right).
