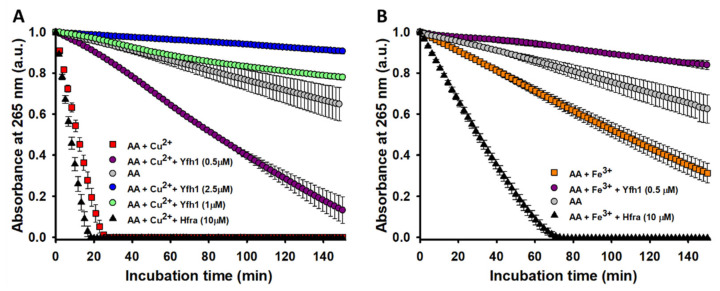
Figure 2.
Effect of Hfra and Yfh1 on the Cu2+- and Fe3+-catalyzed degradation rate of AA. (A) Time-dependent AA (70 μM) degradation at 25 °C measured by the decrease in its absorbance at 265 nm when AA was alone (●), in presence of Cu2+ (2.5 μM) (■), in the presence of Cu2+ (2.5 μM) and Yfh1 (0.5 μM) (●), in the presence of Cu2+ (2.5 μM) and Yfh1 (1 μM) (●), in the presence of Cu2+ (2.5 μM) and Yfh1 (2.5 μM) (●), and in the presence of Cu2+ (2.5 μM) and Hfra (10 μM) (▲). (B) Time-dependent AA (70 μM) degradation at 25 °C measured by the decrease in its absorbance at 265 nm when AA was alone (●), in presence of Fe3+ (2.5 μM) (■), in the presence of Fe3+ (2.5 μM) and Yfh1 (0.5 μM) (●), and in the presence of Fe3+ (2.5 μM) and Hfra (10 μM) (▲). In both panels, the data points are the mean from all the replicas, and the error bars represent standard deviation from the different independent measurements.