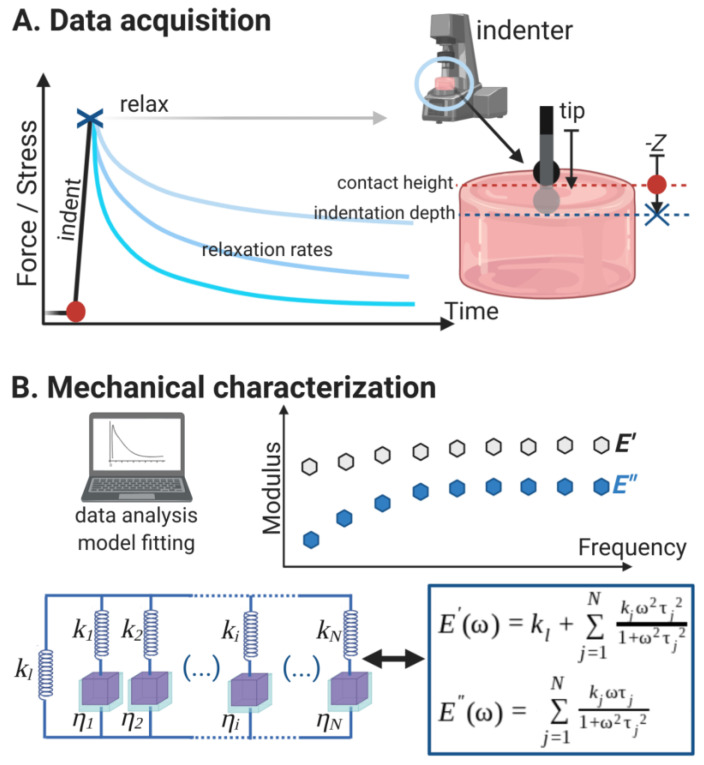
Figure 1.
Diagram (not to scale) of the method employed here to study with great precision the mechanical properties and dynamic behavior of polyacrylamide (PAM) hydrogels used in mechanobiology assays. (A) Relaxation test performed with a microindenter; it collects all the information necessary to analyze the hydrogels mechanically. The bead is typically 50 µm in diameter and the gel ~200 µm thick. (B) The data collected from the relaxation test is adjusted using a generalized Maxwell model (GMM) with the appropriate relaxation times τi that then allows to obtain the corresponding ki and ηi. The long term stiffness kl (or k∞) is also determined from the model fitting. Finally, the dynamic storage (E′) and loss (E″) moduli that describe the soft material were calculated, assuming a linear viscoelastic behavior. This complete characterization is more accurate than a microindentation and calculation of the elastic (Young’s) modulus.