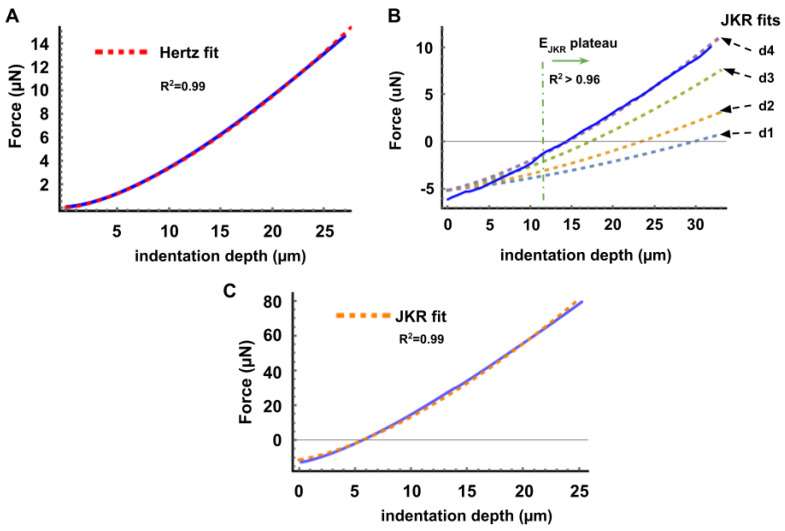
Figure A3.
Representative curves of FD fitting processing. (A) Hertz model fitting of the indentation of a 4 kPa PAM hydrogel in ddH2O + 0.1% Extran. The viscous drag was calculated using the slope of the approach curve (Figure 2C in the main text) obtaining 0.006 ± 0.005 µN/µm at an indentation speed of 100 µm/s, which is negligible compared to the ~0.3 µN change due to relaxation with the same indentation speed. (B) JKR model fitting of the indentation of the same hydrogel PAM measured while only soaked. There is an underestimation of the slope (therefore the elastic modulus) when modelling data with distances lower than ~10 µm. Also, for indentation depths greater than ~11 µm the Young’s modulus reaches a plateau value which is similar to the behavior presented in Figure 3 in the main text. (C) JKR model fitting of a stiffer hydrogel (~35 kPa, see Table 1) when only soaked in deionized water. There is a clear attraction of ~10 µN, twice that of the softer PAM hydrogel (~5 µN), suggesting a possible dependency of the tip attraction with the stiffness of the sample (acrylamide/bisacrylamide proportions).