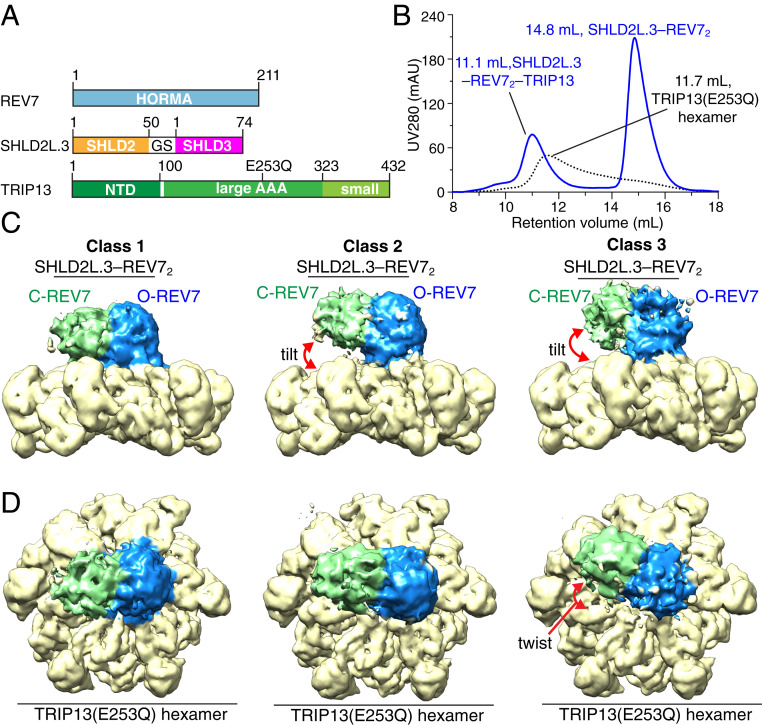
Fig. 6.
Cryo-EM structure of SHLD2L.3–REV72–TRIP13(E253Q) complex. (A) Schematic drawing of REV7, SHLD2L.3, and TRIP13 (E253Q) proteins involved in complex formation. Note that SHLDL2.3 contains a longer version (residues 1 to 50) of SHLD2 compared with SHLD2.3 (residues 1 to 19 of SHLD2). (B) Copurification of the complex formed by TRIP13(E253Q) hexamer and SHLD2L.3–REV72 in the presence of ATPγS by size exclusion chromatography. (C and D) The overall structure of the SHLD2L.3–REV72–TRIP13(E253Q) complex with bound ATPγS shown in electron density representations. Three different classes of structures of the complex with different twist and tilt between the SHLD2L.3–REV72 and TRIP13 (E253Q) components are shown with side (C) and top (D) views.