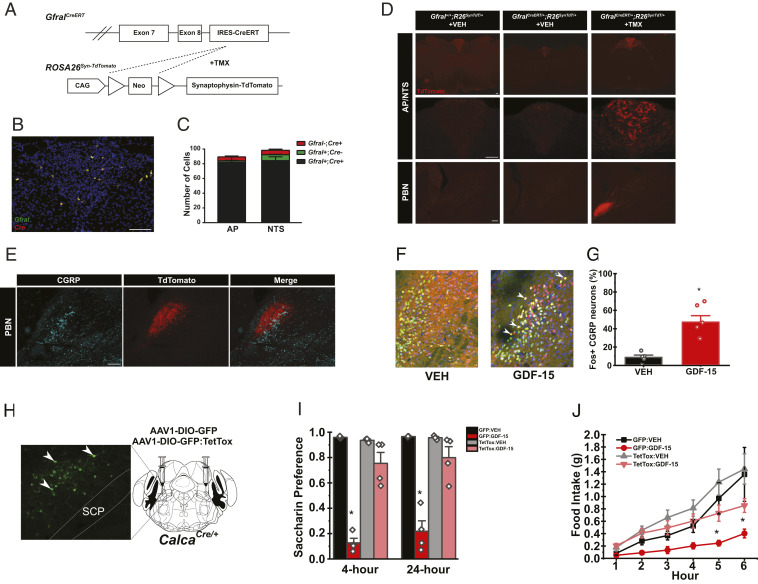
Fig. 4.
AP GFRAL neurons project to the PBN and CGRPPBN neurons are required for GDF-15-mediated feeding suppression and aversion (A) Schematic of GfralCreERT– and TMX-mediated recombination of the Lox-Stop-Lox cassette from the ROSA26Syn-TdTomato line to generate GFRALCreERT-TdTomato mice. (B and C) Representative image and quantification of ISHs for Cre (red) and Gfral (green) transcripts in the AP/NTS of GfralCreERT/CreERT mice (n = 3). (D) Representative image of TdTomato-IR (red) in AP/NTS and PBN of Gfral+/+ mice, GFRALCreERT-SynTdT mice, and GFRALCreERT-SynTdT mice administered TMX or VEH, as indicated. (E) Representative image of TdTomato- (red) and CGRP-IR (cyan) within the PBN from TMX-treated GFRALCreERT-SynTdT mice. (F and G) Representative images (F) and quantification (G) of PBN FOS-IR 4 h following VEH or GDF-15 (400 μg/kg) administration (DNA: blue, CGRP: green, and FOS: red; n = 5). (H) Verification of GFP:TetTox expression within the PBN of CalcaCre mice (Green: GFP). (I) CTA in AAV-DIO-GFP or AAV-DIO-GFP:TetTox injected CalcaCre:GFP/+ mice administered with either VEH or GDF-15 during conditioning (n = 4). (J) Dark phase food intake of in AAV-DIO-GFP or AAV-DIO-GFP:TetTox injected CalcaCre:GFP mice injected with either VEH or GDF-15 1 h prior to the onset of the dark cycle (n = 5). SCP= superior cerebellar peduncle. Data are shown as mean ± SEM and analyzed by Two-way ANOVA *P < 0.05. (Scale bar, 100 μm.)