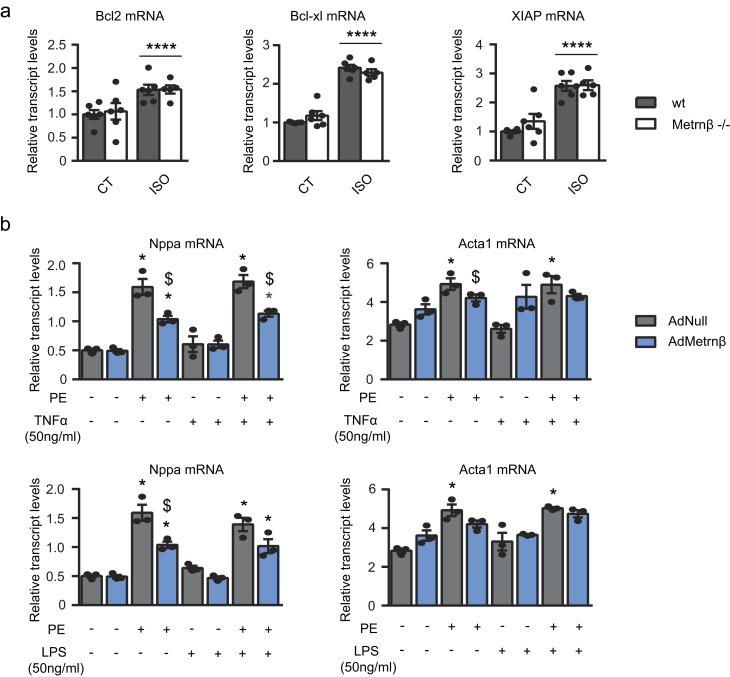
Figure S2.
Role of Metrnβ in apoptotic and pro-inflammatory pathways. (a) 2-mo-old WT littermates (gray bars) and Metrnβ−/− (white bars) mice were continuously infused with ISO for 7 d to experimentally induce heart hypertrophy. mRNA expression levels of antiapoptotic genes Bcl2, Bcl-xl, and Xiap in the myocardium. n = 6 mice/group. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA (****, P < 0.00001 compared with corresponding control [CT] mice). (b) mRNA expression levels of the hypertrophy markers Nppa and Acta1 in NCMs after PE-induced hypertrophy alone or with TNFα or LPS in NCMs overexpressing Metrnβ (Ad-Metrnβ; blue bars) or Ad-null control vector (10 IFU/cell; gray bars). Cell culture experiments were conducted on three independent cardiomyocyte isolations. Data were analyzed by Student’s t test. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (P values are 0.0015, 0.02, 0.001, 0.0036, 0.003, 0.011, 0.0028, 0.0492, 0.0096, 0.0015, 0.02, 0.001, 0.0035, 0.0114, 0.0028, 0.0196; *, P < 0.05 compared with control cells; $, P < 0.05 compared with PE-treated cells).