Figure 7: Limiting ATF6α signaling attenuates ER-stress mediated inflammation in human organoids.
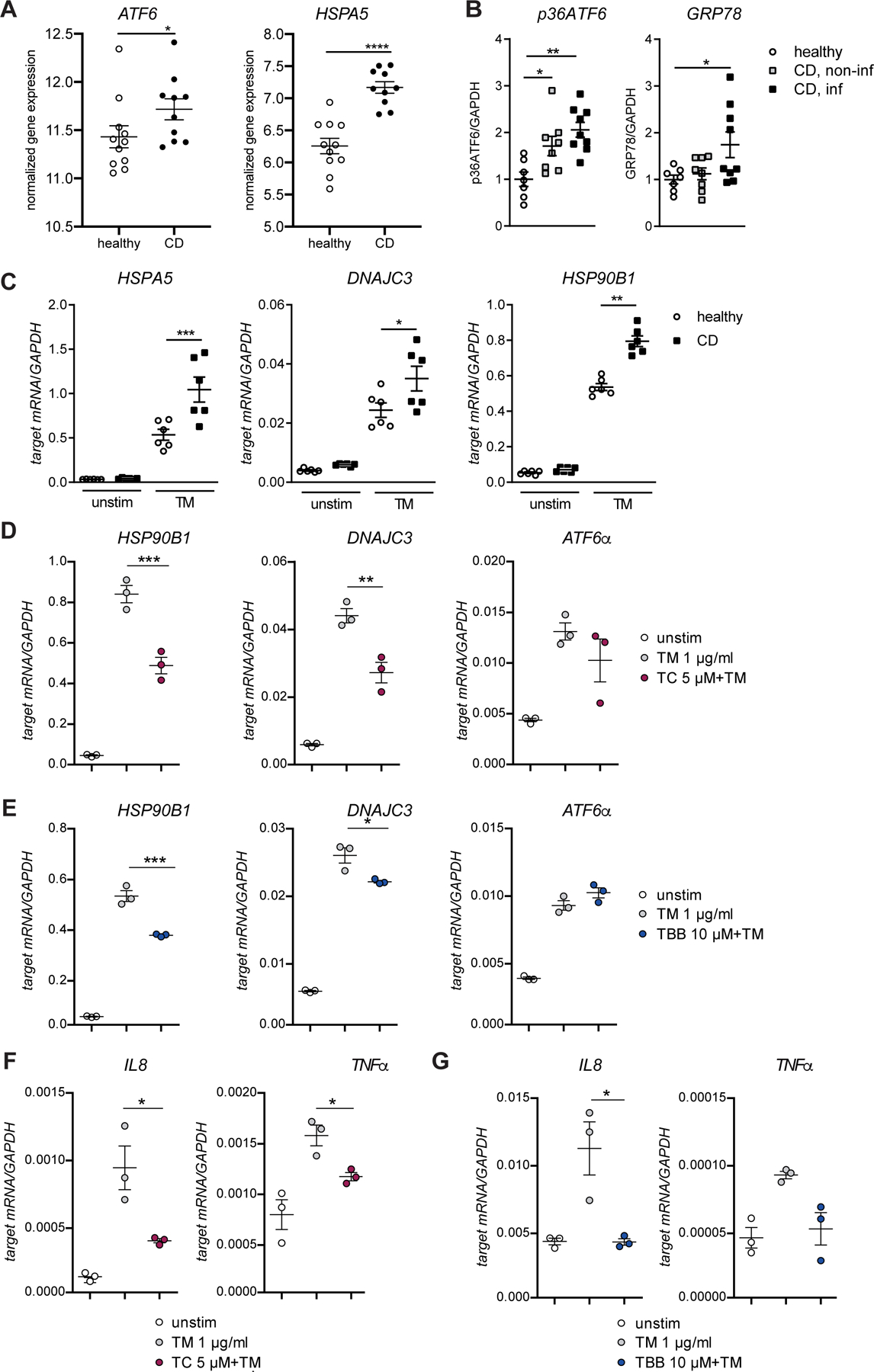
(A) Relative mRNA expression of ATF6α and HSPA5 in IECs from ileal biopsies from paediatric CD patients and healthy controls. (B) Quantification of protein levels of p36ATF6 and GRP78 derived from SI organoid lysates generated from healthy, CD non-inflamed, and CD inflamed tissue, respectively. (C) mRNA levels of HSPA5, DNAJC3, and HSP90B1 in human SI organoids from healthy controls and CD patients treated with tunicamycin (1 µg/ml; 24 h). (D) Transcript levels of HSP90B1 and DNAJC3 in human SI organoids treated with tunicamycin (1 µg/ml) and TC (D) or TBB (E) for 24 h. (F–G) IL8 and TNFα transcript levels in human SI organoids treated with tunicamycin (1 µg/ml) and inhibitor TC (F) or TBB (G), respectively (24 h, n=3). Depicted data representative of 3 independent experiments. Each data point represents one organoid line derived from an individual CD patient. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA together with Tukey post hoc test or Mann-Whitney test (for pair comparisons).
