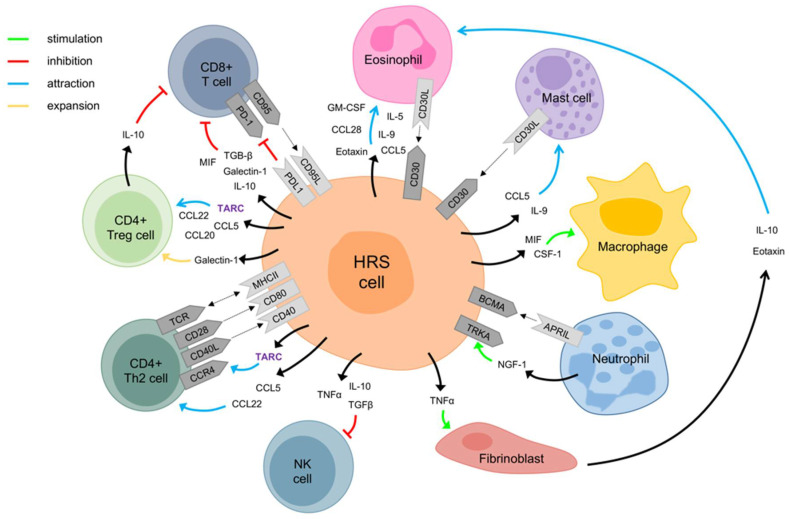
Figure 1.
The figure shows interactions between Hodgkin and Reed–Sternberg (HRS) cells and the tumor microenvironment (direct cellular interactions and via soluble mediators). Many different cell types are attracted into the microenvironment by chemo- and cytokines. HRS cells attract CD4+ type 2 T helper (Th2) cells through secretion of the chemokines TARC, CC chemokine 5 (CCL5) and CCL22. These, as well as CCL20, also attract CD4+ regulatory T (Treg) cells. HRS cells are stimulated by neutrophils through APRIL-BCMA interaction and secretion of nerve growth factor-1 (NGF-1). NGF-1 binds to the receptor tyrosine kinase (TRKA) on HRS cells. HRS cells are also stimulated by mast cells and eosinophils by CD30-CD30 ligand interaction. CD8+ T cells, also known as cytotoxic T cells, are inhibited by IL-10, produced by Treg cells. HRS cells also inhibit CD8+ T cells and NK cells through IL-10 and other immunosuppressive mediators and expression of the programmed cell death 1 ligand (PD1L).