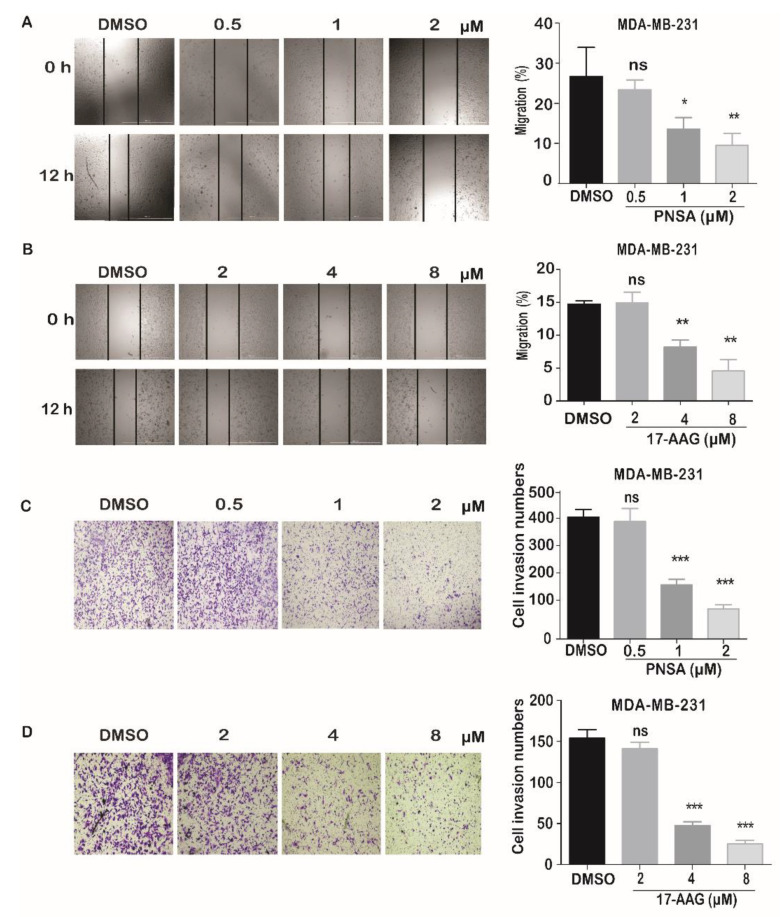
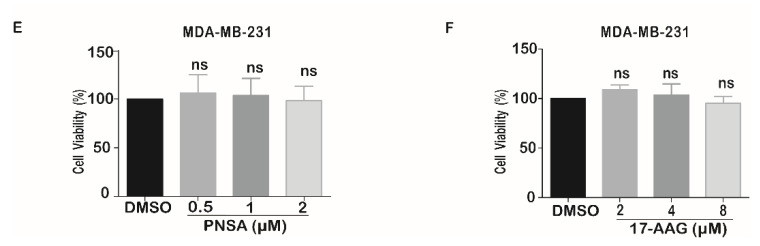
Figure 2.
PNSA inhibits the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. (A,B) Inhibition effects of PNSA and 17-allyl-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG) on the migration of MDA-MB-231 cells. Representative images of the wound healing assay performed with MDA-MB-231 cells treated with indicated concentrations of PNSA (A) or 17-AAG (B), the migrated ratio was calculated (right panels). (C,D) Inhibition effects of PNSA and 17-AAG on the invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells. The MDA-MB-231 cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of PNSA (C) or 17-AAG (D) for 12 h through a Matrigel-coated Boyden Chamber, the invasion cells were counted (right panels). (E,F) Effects of PNSA and 17-AAG on the viability of MDA-MB-231 cells. Cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of PNSA (E) or 17-AAG (F) for 12 h and cell viability was measured using sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay. The bar graph represents the average ± SD of at least three independent experiments. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; ns, not significant (relative to DMSO-treated cells).