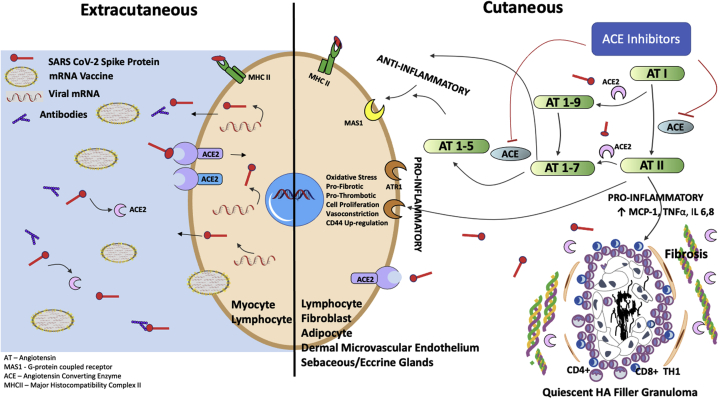
Fig 4.
Proposed mechanism of action of ACE-I acting on the cutaneous RAS to decrease AngII, in the setting of post COVID-19 vaccination, with reduction of AngII-induced proinflammatory pathway stimulation of DIR to residual hyaluronic acid filler. ACE, Angiotensin-converting enzyme; ACE-I, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme receptor; AngII, angiotensin II; AT, angiotensin; ATR1, angiotensin II receptor type 1; DIR, delayed inflammatory reaction; HA, hyaluronic acid; IL, interleukin; MAS1, G-coupled protein receptor; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein type 1; MHCII, major histocompatibility complex I/II; RAS, renin-angiotensin system; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α. (A portion of this figure was adapted from Jaume Alijotas-Reig et al. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013; Aug;45(1):97-108.)