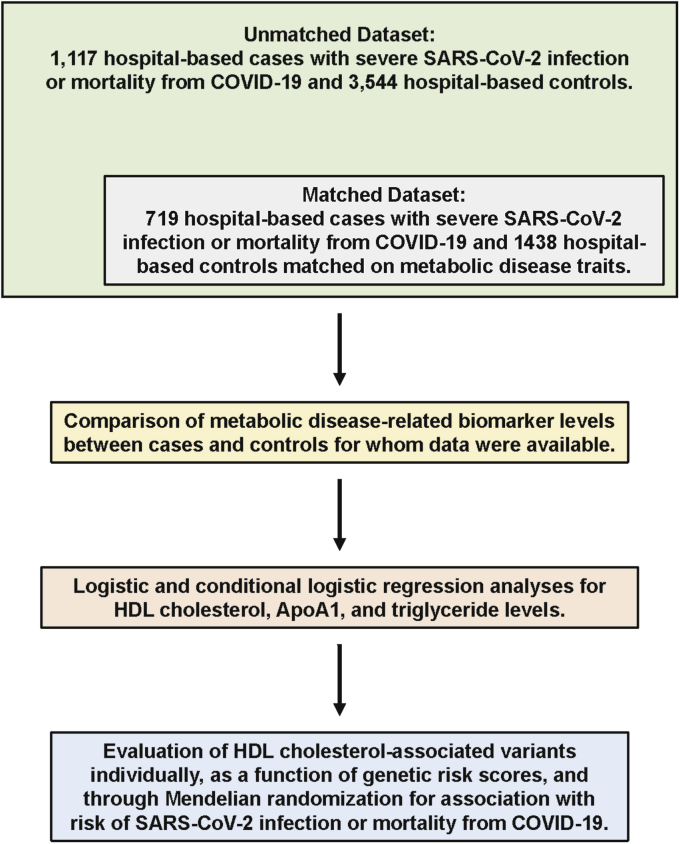
Fig. 1.
Overview of clinical and genetic analyses. A study was designed using data made available by the UK Biobank where cases were defined as symptomatic subjects who tested positive for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in a hospital setting or whose cause of death was attributed to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) (green box). Unmatched controls were defined as subjects who tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 infection in inpatient or outpatient hospital settings. A subset of these subjects was used for a data set where controls were matched to cases at a ratio of 2:1 based on complete data for age, sex, obesity, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and coronary artery disease (gray box). Comparisons of differences in nine metabolic disease-related biomarker levels between cases and controls (yellow box) were followed by logistic regression analyses with HDL-cholesterol, ApoA1, and triglyceride levels (pink box). Previously identified genetic variants associated with HDL-cholesterol levels were then evaluated for association with risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection or mortality from COVID-19 using various analytical strategies (blue box).