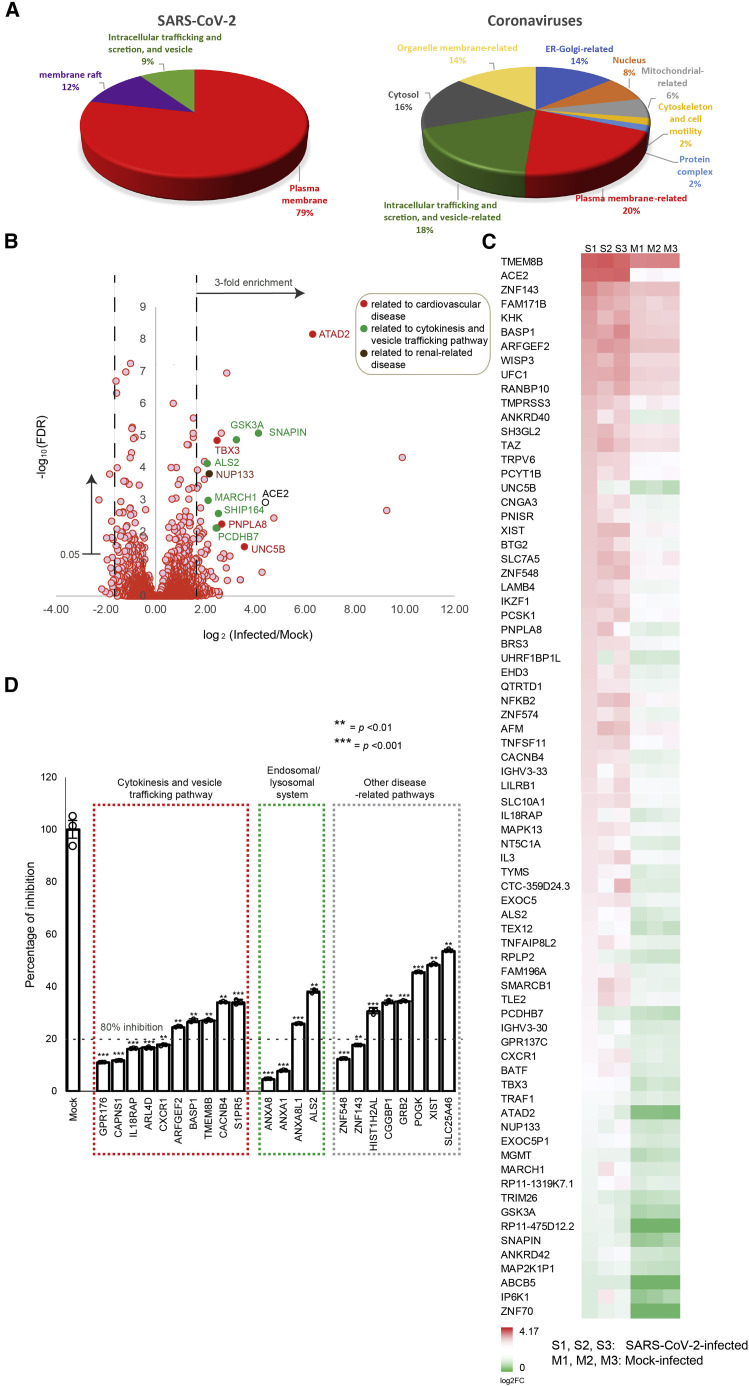
Figure 3.
VDFs related to cytokinesis, vesicle trafficking, and endosomal/lysosomal system are important for SARS-CoV-2 infection
(A) Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of VDFs identified in our RNAi screening (left) and that reported by other coronavirus studies (right) using a threshold p value of 0.05. The percentage of each GO term is shown in pie charts.
(B) Volcano plot analysis of VDFs identified in our RNAi screening. Gene annotation revealed that some enriched VDFs ≥3-fold enrichment and false positive rates (FDRs) <5% have functional roles related to the regulation of the cardiovascular system (filled red), cytokinesis and vesicle trafficking pathway (filled green), and renal-related disease (filled brown).
(C) Heatmap analysis of the ≥3-fold enriched VDFs with FDRs < 0.05. S1–3 and M1–3 are biological replicates of SARS-CoV-2- and mock-infected samples, respectively.
(D) siRNA knockdown of selected VDFs in HK-2 cells leads to an inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 replication as assessed by qRT-PCR. Transfection of non-targeting siRNA was included as negative control (mock). Data points below the dotted line indicate siRNA inhibitory effects on SARS-CoV-2 infection to be >80%. The results were derived from three independent experiments. Each data point and error bar depict the mean value and SEM, respectively. Statistical analyses were carried out using Student’s t test. Statistical significance is indicated by the asterisks (∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001).