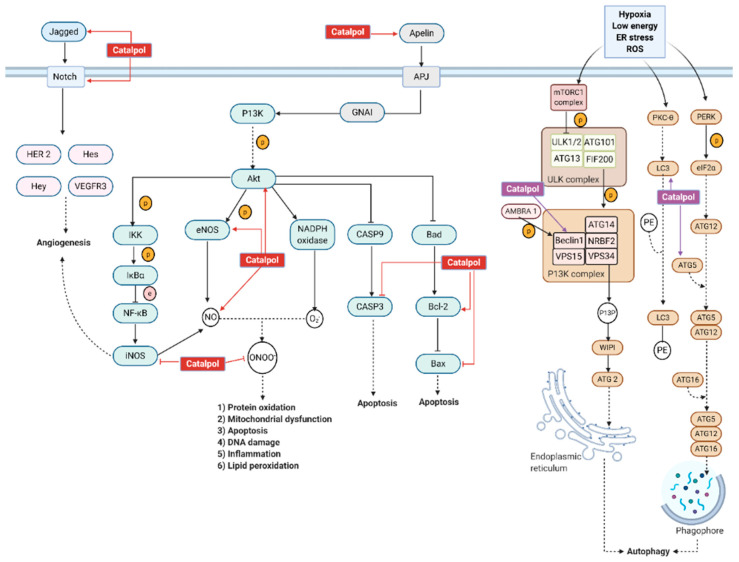
Figure 9.
Cardioprotective mechanism of catalpol in MI. Catalpol is able to upregulate Notch/Jagged pathway to stimulate angiogenesis after MI. Catalpol could also upregulate Apelin/APJ signaling pathway to exert cardioprotective effect. Activation of APJ later activates P13K/Akt pathway. APJ is involved in regulating Akt/eNOS pathway that could stimulate cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and DNA repair. Moreover, activation of Akt could scavenge the superoxide anion (free radical). NO is an antioxidant and could also exert vasodilation effect. However, under increment of free radicals, NO could react with O2∙ to form ONOO∙. ONOO∙ could further contribute to increase oxidative stress. This later leads to protein oxidation, mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, DNA damage, inflammation, and lipid peroxidation. Catalpol is able to decrease oxidative stress by reducing O2∙, increasing NO, and reducing formation of ONOO∙. Akt activation could prevent apoptosis by inhibiting caspase 9 and Bad. Catalpol further exerts its cardioprotective effect by inhibiting caspase 3 and Bax and upregulating Bcl2. Catalpol is able to upregulate autophagy proteins such as Beclin1, AGT5, and LC3 that promotes autophagy.