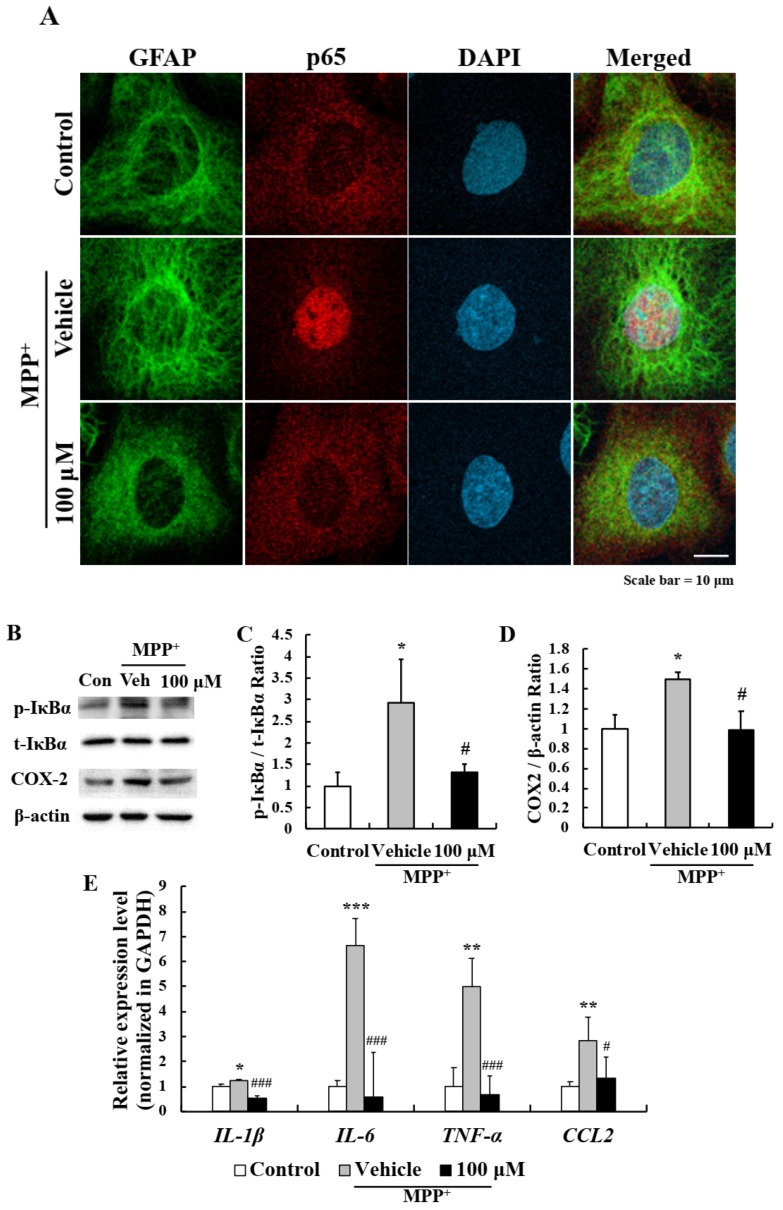
Figure 5.
NF-κB pathway inhibition in primary astrocytes was responsible for the anti-inflammatory effect of EA. (A) Representative images showing that EA inhibited the MPP+-induced nuclear translocation of p65. Scale bar = 10 µm. (B) Western blot showed that EA repressed MPP+-induced IκBα phosphorylation and COX2 expression. (C,D) Bar graphs of fold changes of western blot. Three independent experiments were performed (n = 3). * p < 0.05 vs. naïve controls and # p < 0.05 vs. MPP+ controls (the analysis was performed using ANOVA with Fisher’s PLSD procedure). (E) Real-time PCR showed that EA significantly reduced the expressions of MPP+-induced inflammatory cytokines and chemokine. Values are means ± SEs (n = 3). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. naïve controls and # p < 0.05, ### p < 0.001 vs. MPP+ controls (the analysis was performed using ANOVA with Fisher’s PLSD procedure).