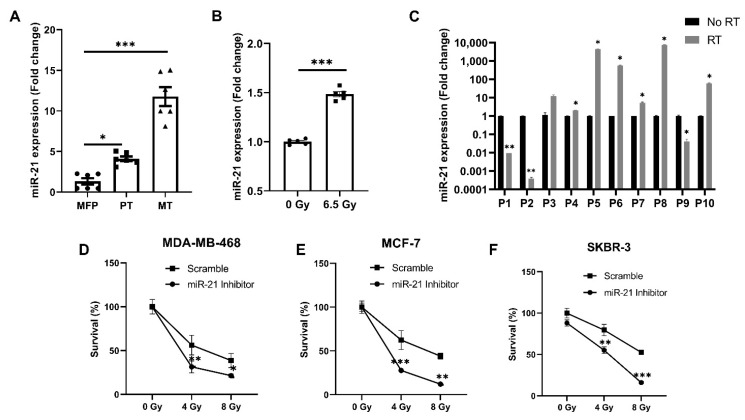
Figure 1.
Stress-activated miR-21 plays a critical role in breast cancer growth and metastases. (A) miR-21 expression was increased as the breast cancer progressed. Basal levels of miR-21 were seen in the normal fat pad, the orthotopic primary tumor showed increased expression of miR-21, and the maximum increase in miR-21 was seen in lung metastases (n = 2 mice/group; ●—Individual replicates for normal mammary fat pad (MFP), ▪—Individual replicates of primary tumor (PT) ▲—Individual replicates of Metastases (MT). (B) Radiation-caused stress induced increases in miR-21 expression in the primary tumor (n = 2 mice/group; ●—Individual replicates for primary tumor without radiation, ▪—Individual replicates of primary tumor irradiated with dose 6.5 Gy). (C) miR-21 expression was increased in human serum post-radiation (n = 10). (D) Knockdown of miR-21 with a specific inhibitor sensitized MDA-MB-468, MCF-7 (E), and SKBR3 (F) cells to increasing doses of radiation over a total treatment period of 72 h (n = 3/group). For (A–C), mean ± SEM with ***, ** are significantly different with p < 0.001 or <0.01 as determined by one-way ANOVA or student’s t-test. For (D–F), mean ± SD with ***, **, * are significantly different with p < 0.001 or < 0.01 or 0.05 as determined by one-way ANOVA or student’s t-test.