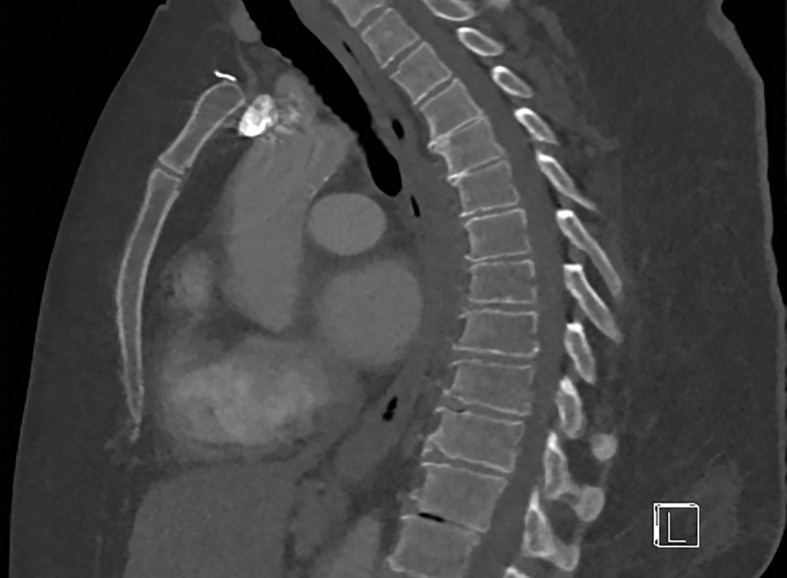
Figure 2b.
Importance of protocol selection. Sagittal single-energy–equivalent CT images of the thorax in a 280-lb (127-kg) patient, obtained with dual-source DECT at the same window display setting at two time points. The images were acquired at tube voltages of 80/140 kVp tin filter (Sn) (volumetric CT dose index = 10 mGy) (a) and 100/150 kVp Sn (volumetric CT dose index = 25 mGy) (b). Image quality is superior in b compared with in a owing to improved photon flux and penetration, at the expense of higher radiation dose.