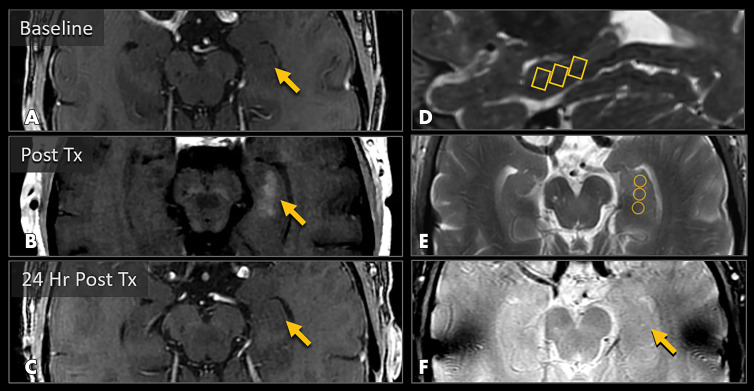
Figure 2:
MRI scans show blood-brain barrier (BBB) opening and closure within targeted brain volumes in a 73-year-old woman with Alzheimer disease. Postcontrast T1-weighted images at, A, baseline, B, immediately after treatment (Tx), and, C, 24 hours after treatment show parenchymal contrast material extravasation (arrow in B) due to BBB opening locally at the treatment sites and BBB closure with resolution of parenchymal contrast enhancement on repeat gadobutrol administration 24 hours later (arrow in C). D, Sagittal T2-weighted image shows three 5 × 5 × 7-mm target volumes demarcating the treated areas within the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. E, Target sites shown on axial T2-weighted image. F, Axial image obtained with the T2* gradient-echo sequence immediately after treatment shows no evidence of signal dropout to suggest hemorrhage at the treated areas.