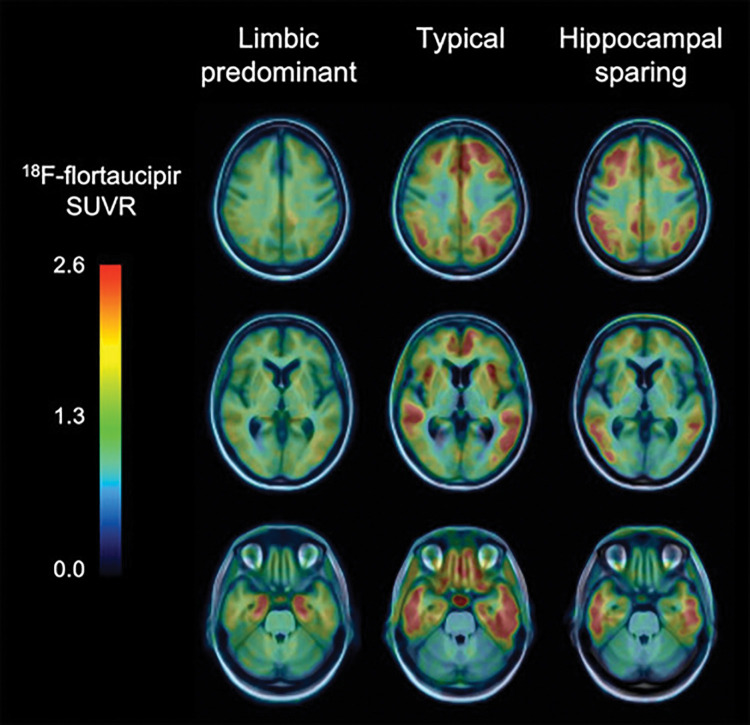
Figure 4:
Tau imaging helps identify pathologic subtypes in Alzheimer disease (AD). Fluorine 18 (18F) flortaucipir PET images in three patients with AD show three different pathologic subtypes of AD: limbic predominant (left column) with tracer retention mostly restricted to mesial temporal lobes, typical presentation (center column) with widespread retention in both mesial temporal lobes and neocortical areas, and hippocampal sparing subtype (right column) where tracer retention is predominantly in neocortex. SUVR = standardized uptake value ratio.