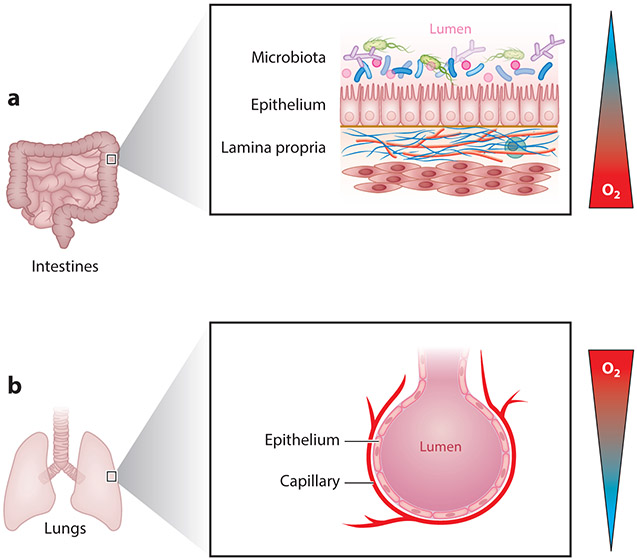
Figure 4.
Opposing mucosal oxygen gradients exist at distinct anatomical barriers. (a) In the gastrointestinal mucosa, a steep oxygen gradient exists from the well-oxygenated capillary bed to the anoxic lumen of the gut, rendering the epithelium in a state of physiologic hypoxia. (b) By contrast, in the alveolar compartment of the lung, a steep oxygen gradient exists from the highly oxygenated lumen of the airway to the subepithelial compartment, where oxygen is efficiently removed.