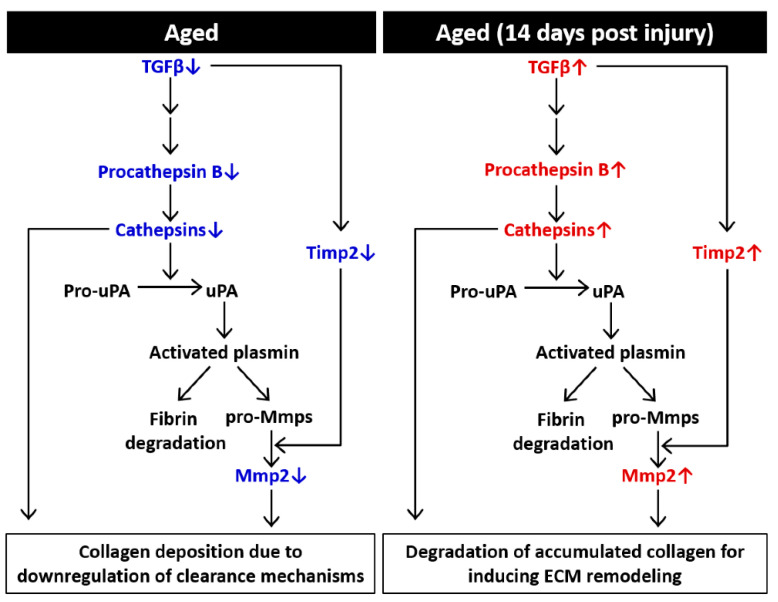
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram showing ECM-mediated effects on remodeling in aged muscle. In aged skeletal muscle, downregulated TGF-β signaling triggers transcriptional changes, including downregulation of procathepsin B and Timp2, which participate in further ECM remodeling. Cathepsins also activate pro-uPA, initiating a uPA-mediated cascade of proteolytic cleavage that results in the activation of plasmin, fibrin and pro-MMPs. After muscle injury, TGF-β induces subsequent transcriptional changes that lead to ECM remodeling, further degradation of collagen and transient deposition of ECM. uPA, urokinase plasminogen activator.