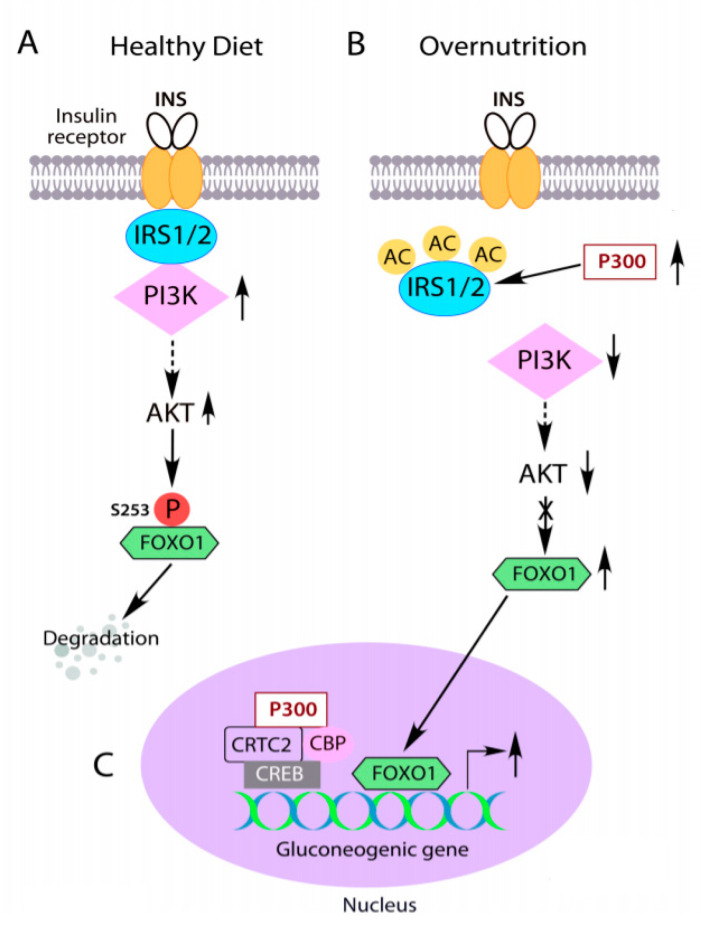
Figure 2.
IRS acetylation by abnormal cytoplasm-appearing P300 causes insulin resistance. (A) Insulin-mediated activation of PI3K-AKT signaling leads to FOXO1 phosphorylation, nuclear exclusion and degradation, subsequently inhibition of gluconeogenic gene expression in the liver. (B, C) Overnutrition induced abnormal cytoplasm-appearing P300 acetylates IRS1 and IRS2 to disrupt their association with insulin receptors and insulin signaling. FOXO1 cannot be phosphorylated by AKT (B), leading to its nuclear accumulation and stimulation of overexpression of the gluconeogenic gene in the liver (C). The solid arrows indicate the direct effects, the dashed arrows indicate indirect effects, and the crossed line indicates the blockade of the pathway.