Fig. 1.
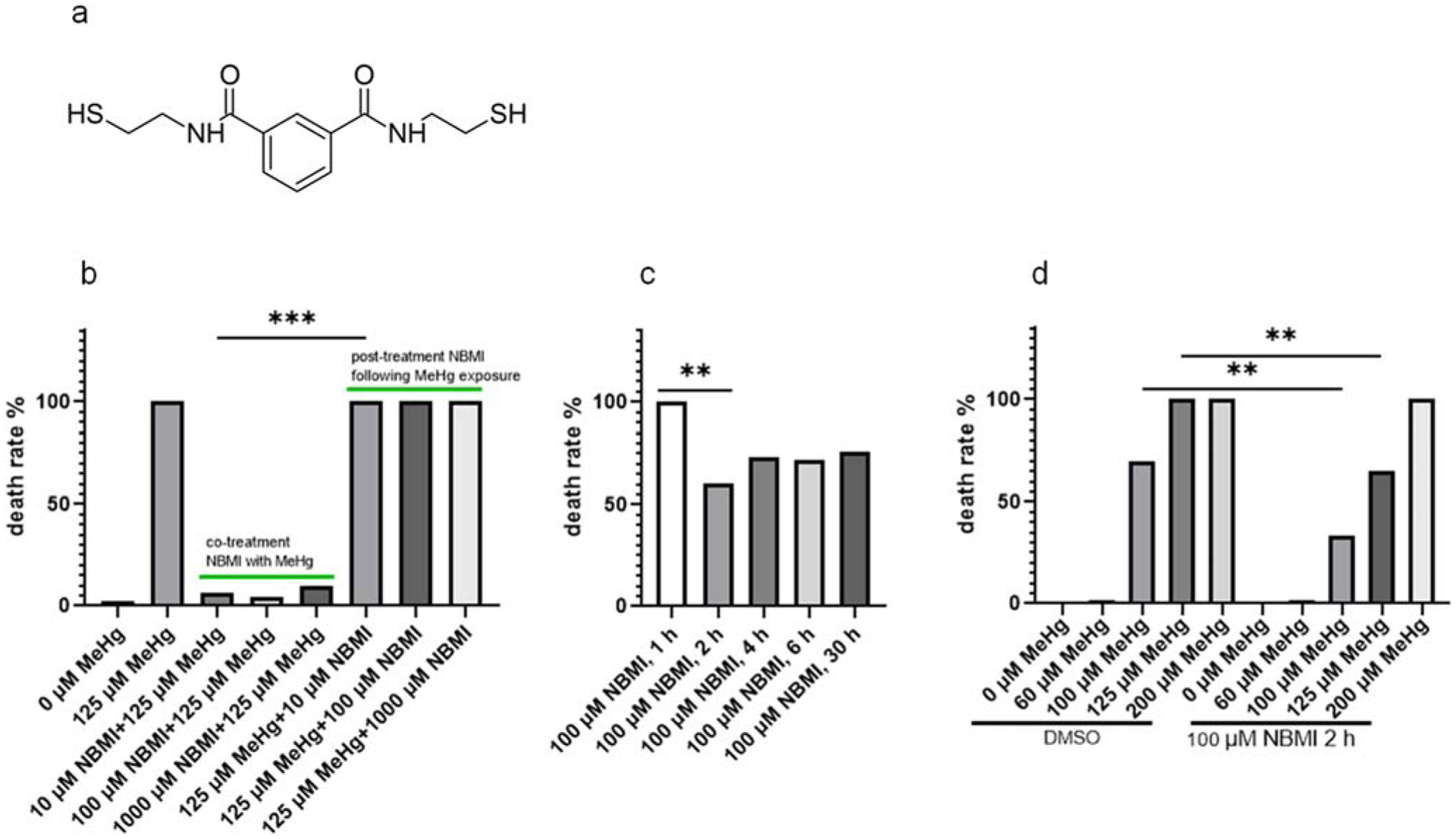
NBMI treatment prevents acute toxicity of MeHg. a Molecular formation and structure of NBMI. b Death rate of worms treated with MeHg and NBMI. For co-treatment NBMI: worms pre-treated with 10–1000 μM NBMI for 1 h, and co-treated with 125 μM MeHg for 1 h. For post-treatment NBMI: worms treated with 125 μM MeHg for 1 h, and post-treated with 10–1000 μM NBMI for 1 h. c Death rate of worms pre-treated with 100 μM NBMI for 0–30 h, and treated with 125 μM MeHg for 1 h in NBMI-free buffer (the medium was replaced before MeHg treatment). d Death rate of worms pre-treated with 100 μM NBMI for 2 h, and treated with 0–200 μM MeHg for 1 h in NBMI-free buffer (the medium was replaced before MeHg treatment). DMSO was used as the vehicle control, which final concentration is 0.1%. Death rate was calculated from 200 to 300 worms per sample. Comparisons of death rate were made with Chi-square test followed by multiple comparisons with Chi-square partition method. The horizontal bars represent a statistical significant difference between the groups with post-hoc multi-comparison test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001
