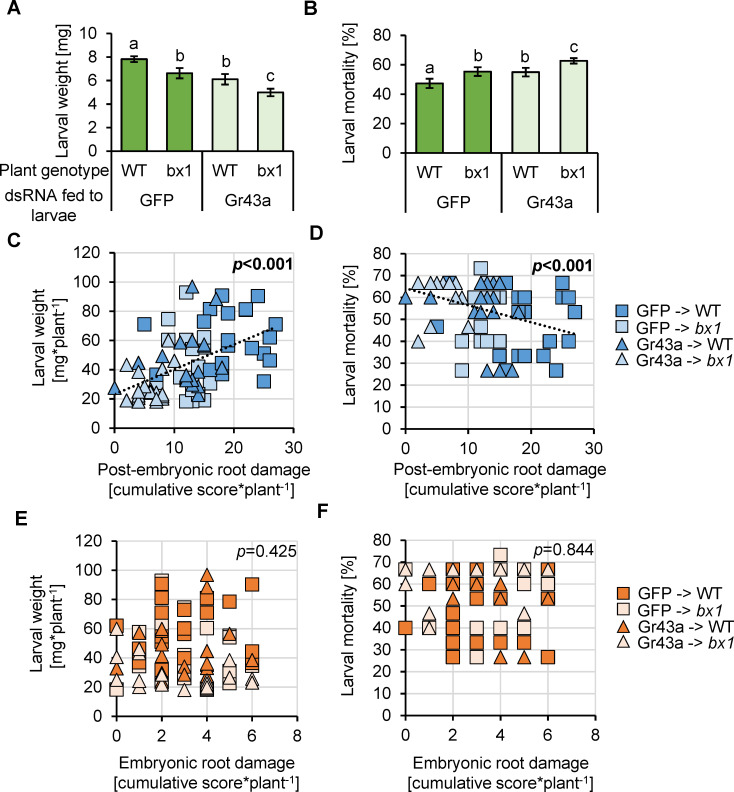
Fig 5. Using benzoxazinoids and sugars as foraging cues improves herbivore growth and survival.
(A) Weight of control (GFP) and DvvGr43a-silenced larvae feeding on WT B73 or bx1 mutant plants for 7 days. Note that in a no-choice situation, neither the bx1 mutation nor DvvGr43a silencing reduce larval performance ([75] and S8 Fig). Letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05, Holm–Sidak post hoc tests, n = 20 pots with 15 larvae each). (B) Larval mortality within the same experiment. Letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05, Holm–Sidak post hoc tests, n = 20 pots with 15 larvae each). (C–F) Correlations between cumulative damage per plant and larval performance parameters for postembryonic roots (C, D) and embryonic roots (E, F). Linear regressions are shown for significant correlations (p < 0.05). P values are shown for Spearman Rank Order correlations. Underlying data can be found in S1 Data. dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; GFP, green fluorescent protein; WT, wild-type.