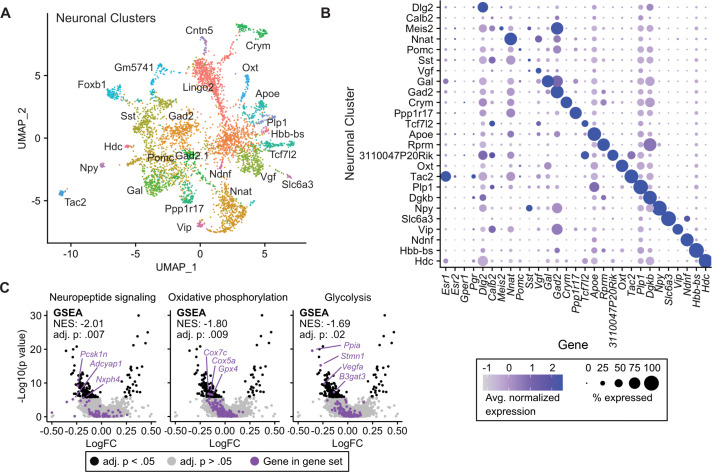
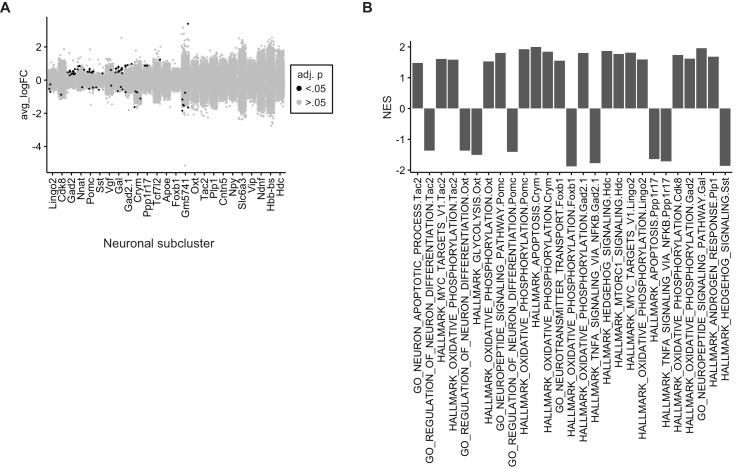
Figure 4. Tamoxifen-induced gene expression changes in neurons of the hypothalamus and preoptic area (hypothalamus-POA).
(A) UMAP showing clustering of the neuronal subtypes of the hypothalamus-POA based on single-cell transcriptomics, overlayed with identity named for top expressed cluster defining marker gene. (B) Dot plot showing expression of neuronal cluster defining markers, Esr1, Esr2, Gper1, and Pgr. (C) Volcano plots of tamoxifen-induced or repressed differentially expressed genes (DEGs) overlayed with gene sets (GS) involved in neuropeptide signaling, oxidative phosphorylation, or glycolysis. Analyses done from wild-type female mice injected daily with oil (n = 3) or tamoxifen (n = 5) over 28 days. NES: Normalized enrichment score, GSEA adj. p: Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted p-value, DEG adj. p: Bonferroni adjusted p-value.