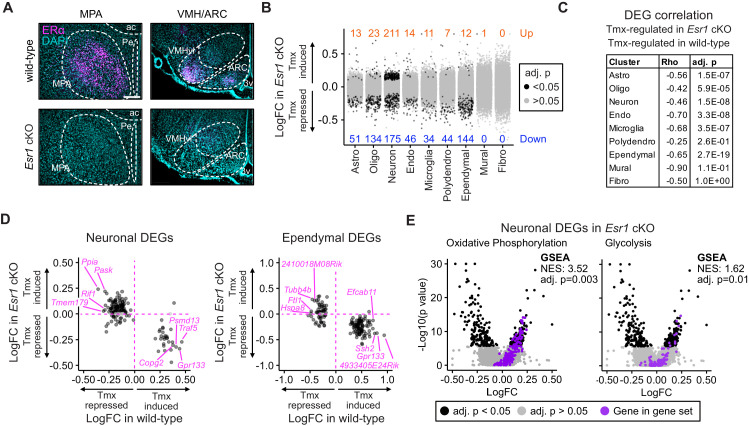
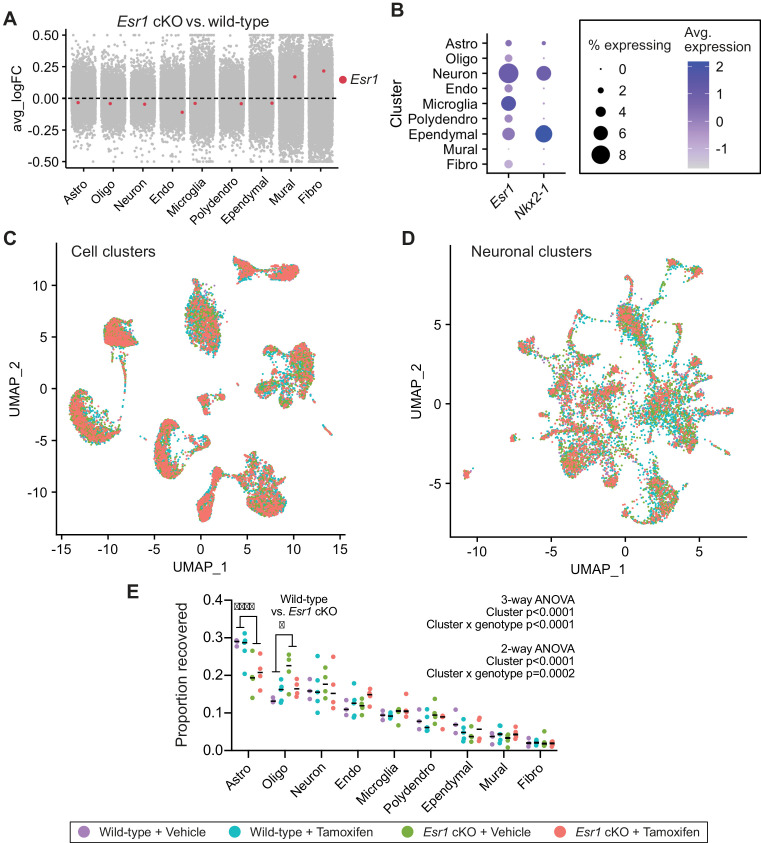
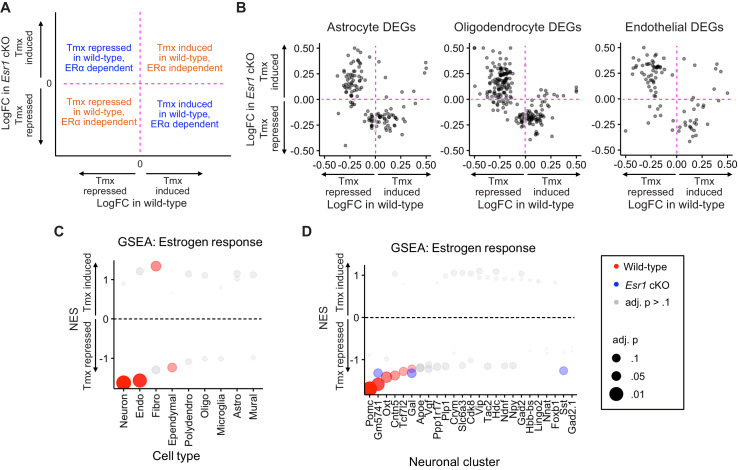
Figure 5. Esr1 conditional knockout reverses hypothalamus and preoptic area (hypothalamus-POA) responses to tamoxifen.
(A) Immunoreactive staining of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) in the medial preoptic area (MPA), ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMH), and the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARC) of ERα knockout and wild-type female mice. Scale bar: 200 um. (B) Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) induced by daily tamoxifen treatment in cell types of the Esr1f/f;Nkx2-1Cre (Esr1 cKO) hypothalamus-POA. Up/down numbers refer to total number of significantly (Bonferroni adj. p<0.05) up- and downregulated genes. (C) Table of correlations showing how tamoxifen-induced gene expression changes in wild-type cells correlate with tamoxifen-induced gene expression changes in Esr1 cKO cells. Rho: Spearman correlation coefficient, adj. p: Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted p-value. (D) Gene-by-gene comparison of how tamoxifen treatment affects expression in wild-type and Esr1 cKO neurons and ependymal cells. Named genes are a subset of genes discordantly regulated by tamoxifen in wild-type and Esr1 cKO cells. A complete list of genes shown here is in Supplementary file 1i. (E) Volcano plots of all tamoxifen-induced or repressed DEGs (black) overlayed with gene sets (purple) involved in oxidative phosphorylation or glycolysis. NES: Normalized enrichment score, gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) adj. p: Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted p-value, DEG adj. p: Bonferroni adjusted p-value. (B–E) Data from n = 4 oil treated Esr1 cKO and n = 4 tamoxifen-treated Esr1 cKO, n = 3 oil treated wild-type and n = 5 tamoxifen-treated wild-type mice.