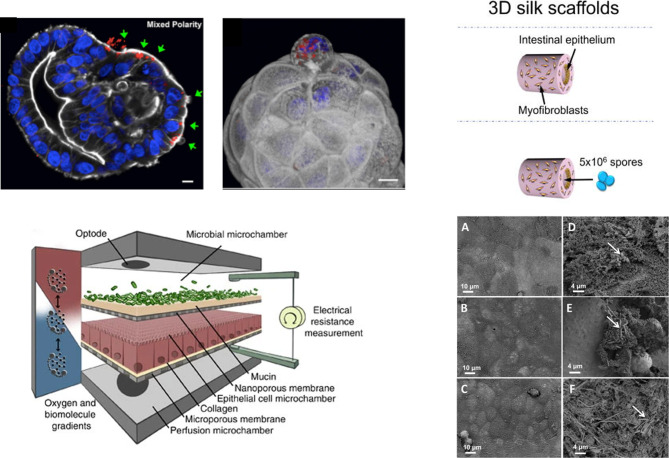
Figure 2. Examples of in vitro human intestinal models for studying host-microbe and host-microbiome interactions.
(A) S. Typhimurium-mCherry infection of human enteroids. Selective invasion of the exposed apical surface (green arrows) of a mixed polarity enteroid (left). 3D confocal reconstruction of S. Typhimurium-mCherry within an epithelial cell in the process of extruding from the apical enteroid surface (right) (nuclei in blue, actin in white). Adapted from [45] under the Creative Commons license; (B) Conceptual diagram of the HuMiX model for the representative co-culture of human epithelial cells with gastrointestinal microbiota. Reproduced from [55], under the Creative Commons license; (C) Schematic of C. difficile infection in the 3D scaffold tissue model (left) and scanning electron microscopy of uninfected (left column) and infected with UK1 C. difficile 3D scaffolds (right column) at 4, 24 and 48 h (right). Adapted from [23].