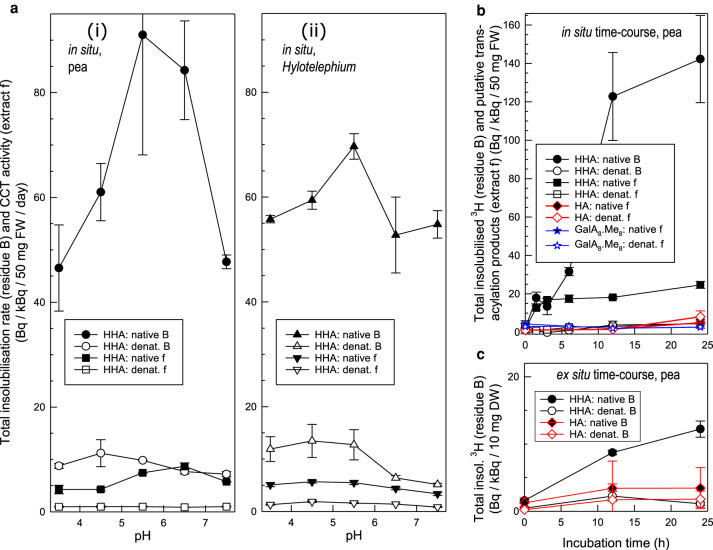
Figure 3. Effect of pH and incubation time on the incorporation of radiolabelled substrates into epidermis in situ and ex situ.
(a) Effect of pH on putative CCT activity in situ in (i) pea epicotyl and (ii) Hylotelephium leaf epidermis. Each native or heat-denatured, blot-dried, 50-mg epidermis sample was incubated with 0.32–0.62 kBq [3H]HHA in 300 µl buffer at 20°C for 24 h. Total methanol-insoluble 3H-products (residue B of Figure 2) were assayed. The material solubilised by alkaline hydrolysis (extract f of Figure 2; putative ester-bonded material) was separately assayed. Filled symbols, native epidermis; open symbols, heat-denatured. Bars indicate standard errors (n = 3). (b) Time-courses of in-situ incorporation of [3H]HHA, [14C]hexadecanoic acid (HA) and Me8-[3H]GalA8-ol (methylesterified oligogalacturonide) by pea epicotyl epidermis at pH 5.5. Methods as in (a), except that the exogenous substrate was 0.10 or 0.13 kBq [3H]HHA, 0.24 kBq [14C]HA or 0.42 kBq Me8-[3H]GalA8-ol. Total 3H-labelled products insoluble in acidified methanol (residue B of Figure 2), and material subsequently alkali-solubilised (extract f; putative ester-bonded material), were assayed for radioactivity. Filled symbols, native epidermis; open symbols, heat-denatured. Data from three independent experiments (±SE, n = 3). (c) Time-course of ex-situ [3H]HHA and [14C]HA incorporation into the total methanol-insoluble fraction of heat-denatured pea epicotyl epidermis (10 mg), catalysed at pH 5.5 by exogenous enzymes extracted from non-denatured pea epicotyl epidermis. Acceptor substrate, 0.64 kBq [3H]HHA or 0.25 kBq [14C]HA. Filled symbols, native protein extract; open symbols, heat-denatured. Bars indicate standard errors (n = 3).