Table 2. In vitro properties of viral protein cargo-targeted inhibitors with antiviral effects.
| Compound | Documented action (IC50) | Antiviral against | Effective concentration (assay, host)/fold reduction in virus production (assay, host cell line) |
|---|---|---|---|
Mifepristone1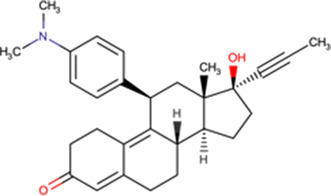
|
Inhibits interaction in vitro of HIV IN with Impα/β (27 μM) [14] Binds to HIV IN core domain but not Impα/β (HSQC NMR) [37] 50 μM inhibits GFP-HIV-1 IN nuclear accumulation in transfected cells [14] 5 μM reduces HIV-1 IN nuclear accumulation > 5-fold in in vitro reconstituted nuclear transport assay [37] 5 μM reduces VEEV CP nuclear accumulation in infected cells [51] Reduces rate/extent of VEEV CP-GFP nuclear import (FRAP) [52] 50 μM reduces HAdV genome nuclear import (cellular fractionation/qPCR) [53] |
HIV-1 | 10 μM > 8-fold (EGFP reporter virus, CEMx174) [50] 10 μM >20-fold (ELISA, PBMC) [50] 200 μM > 3-fold (luciferase, HeLa) [42] |
| VEEV | EC50 = 19.9 μM (PFU, Vero) [52] 10 μM > 10-fold (PFU, U87MG) [51] 10 μM > 5-fold (PFU, Vero) [51] 10 μM > 15-fold (PFU, Vero) [52] |
||
| Human adenovirus HAdV5 |
EC50 = 2 μM (PFU) [53] | ||
Mifepristone analogue 502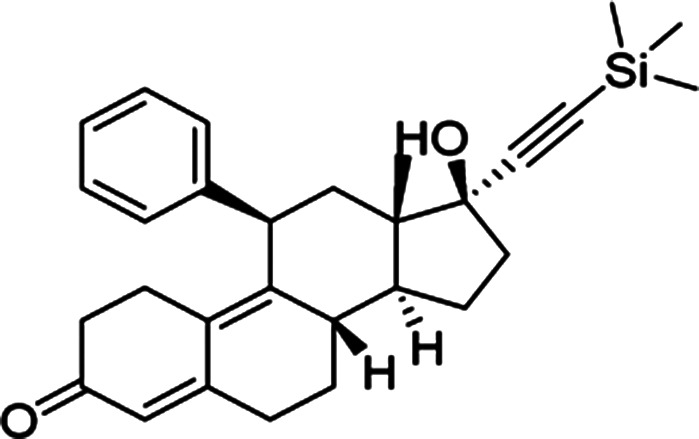
|
50 μM inhibits nuclear import of transfected GFP-CP (FRAP) Reduces recovery of VEEV CP-GFP nuclear fluorescence after FRAP [52] 50 μM inhibits nuclear accumulation of CP in infected cells [52] |
VEEV | EC50 = 7.2 μM (luciferase, Vero) [52] 10 μM > 7-fold (PFU, Vero) [52] |
Budesonide3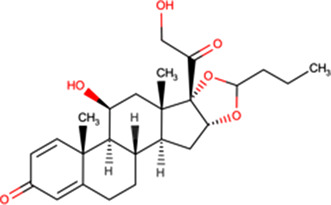
|
Inhibits interaction in vitro of HIV IN with Impα/β (1.2 μM) [37] Binds to HIV IN core domain but not Impα/β (HSQC NMR) [37] 5 μM reduces HIV-1 IN nuclear accumulation > 2-fold in in vitro reconstituted nuclear transport assay [37] 100 μM inhibits HIV PIC nuclear import [37] |
HIV-1 | EC50 = 79.4 μM (luciferase, MT-2, single cycle) [37] EC50 = 49.4 μM (luciferase, TZMbl) [37] |
Flunisolide4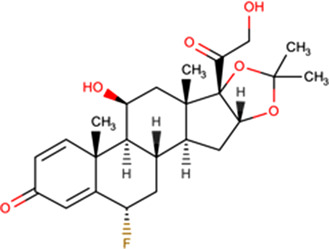
|
Inhibits interaction in vitro of HIV IN with Impα/β (1.4 μM) [37] Binds to HIV IN core domain but not Impα/β (HSQC NMR) [37] 250 μM inhibits HIV PIC nuclear import [37] |
HIV-1 | EC50 = 77.5 μM (luciferase, MT-2, single cycle) [37] EC50 = 105 μM (luciferase, TZMbl) [37] |
G281-1564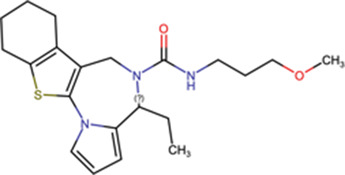
|
Inhibits interaction in vitro of VEEV CP and Impα/β (12 μM) [16] 50 μM inhibits extent and rate of GFP-CP nuclear accumulation in transfected cells (1.8-fold, 1.4-fold, respectively) [16] |
VEEV | EC50 = 10.8 μM (luciferase, Vero)5 [16] 50 μM > 10-fold (PFU, Vero) [16] |
N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide/fenretinide/4-HPR6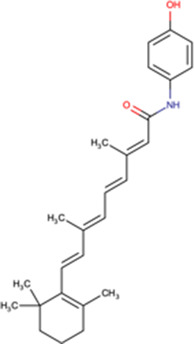
|
Inhibits interaction in vitro of DENV1 NS5:Impα/β (2.3 μM) [82]; DENV2 NS5:Impα/β (0.8 μM) [15]; DENV2 NS5:ImpαΔIBB (1.1 μM) [15]; ZIKV NS5:Impα/β (1.1 μM) [87] Inhibition of DENV2 NS5 nuclear accumulation in infected cells [15,47,77] Destabilises DENV 3 NS5 RdRp (thermostability assay) [44,47] 15 μM inhibits nuclear accumulation of influenza vRNPs (IF) [11] |
Flaviviruses DENV1 (EDEN1) |
EC50 = 2.6 μM (PFU, Huh-7) [15] EC50 (ADE7) = 0.8 μM (PFU, THP-1) [15] EC50 (ADE7) = 0.8 μM (PFU, PBMC) [15] |
| DENV2 (EDEN2) | EC50 = 2.1 μM (PFU, Huh-7) [15] | ||
| DENV2 (NGC) | EC90 = 2.0 μM (PFU, Vero) [77] | ||
| DENV3 (EDEN3) | EC50 = 1.4 μM (PFU, Huh-7) [15] | ||
| DENV4 (EDEN4) | EC50 = 2.1 μM (PFU, Huh-7) [15] | ||
| ZIKV (Asian/Cook Islands/2014) | EC50 = 2.6 μM (PFU, Vero) [87] | ||
| ZIKV (Asian/PF13-251013-1) | EC90 = 1 μM (PFU, multiple hosts) [78] | ||
| ZIKV (African/ MR-766) | 10 μM > 1000-fold (PFU, Vero) [78] | ||
| WNV (Kunjin) | 10 μM > 7-fold (PFU, Vero) [15] 10 μM > 100-fold (PFU, Vero) [77] 10 μM > 10-fold (PFU, Vero) [49] |
||
| YFV | 3 μM > 100-fold (BHK-21, PFU) [46] | ||
| Alphavirus CHIKV |
EC50 = 0.5/3.1 μM (PFU, multiple hosts) [46] | ||
| Modoc | 10 μM >100-fold (PFU, Vero) [77] | ||
| Influenza VLPs8 (avian influenza A/MxA escape mutants) | 10 μM > 4-fold inhibition (luciferase) [11] |
Approved for human use in medical termination of pregnancy, hyperglycaemia treatment in Cushing's syndrome patients;
Analogue of mifepristone ((8S,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-11-phenyl-17-((trimethylsilyl) ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,13, 14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a] phenanthren-3-one)) lacking progesterone receptor antagonism [52];
Approved for asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, allergic rhinitis and nasal polyps, inflammatory bowel diseases;
Approved for the treatment of asthma, allergic rhinitis;
Selectivity index > 9.3;
Progressed to clinical trials (incl. Phase III) for indications including breast, bladder and paediatric cancers, macular degeneration; other actions include increased phosphorylation of eIF2α, promoting an antiviral state not related to long-chain ceramide biosynthesis, PERK pathway or ATF-4 [15,55,77];
ADE model uses subneutralising concentrations of anti-E protein antibody prior to infection;
Mechanism of action against influenza to be determined.
Abbreviations (see Table 1): ADE, antibody-dependent enhancement of infection; DENV, Dengue virus; CFI, cell-based flavivirus infection assay (immunostaining for virus); CoIP, co-immunoprecipitation; CP, capsid protein; CPE, cytopathogenic effect (host cell); CHIKV, Chikungunya virus; EC50, half-maximal effective concentration; Est., estimated; FRAP, fluorescence recovery after photobleaching; FRET, fluorescence resonance energy transfer; GFP, green fluorescent protein; HAdV, human adenovirus; hCMV, human cytomegalovirus; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HSQ NMR, heteronuclear single quantum coherence nuclear magnetic resonance; IBB, importin β-binding domain; IC50, half-maximal inhibitory concentration; IF, immunofluorescence; IN, integrase; lum, luminescence assay; NS5, non-structural protein 5; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PIC, preintegration complex; PFU, plaque forming units (infectious virus); PRV, pseudorabies virus; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; SV40, Simian virus 40; T-ag, SV40 large T-antigen; TCID, tissue culture infectious dose (estimation of viral load based on CPE); VEEV, Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus; VLP, virus-like particle; vRNP, viral ribonucleoprotein complex; VSV-G, vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein; WNV, West Nile virus; YFV, Yellow Fever virus; ZIKV, Zika virus.
