Figure 1.
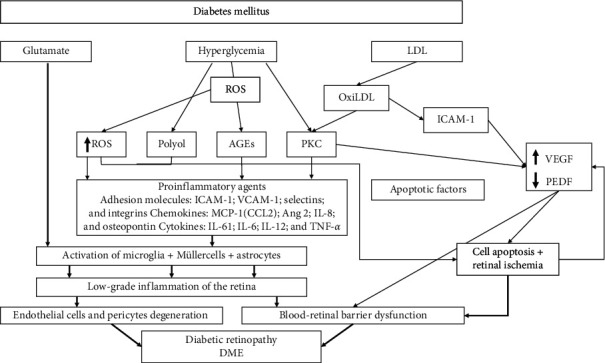
An overview of the different pathways involved in the development of diabetic macular edema (adapted from Daruich et al. [8] and Romero-Aroca et al. [9]). LDL: low-density lipoprotein; ROS: reactive oxidative species; Oxi: oxidized; AGEs: advanced glycation end-products; PKC: protein kinase C; ICAM-1: inflammatory intercellular adhesion molecule-1; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; VCAM-1: vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; PEDF: pigment epithelium-derived factor; CCL2: chemokine C-C motif ligand 2; Ang-2: angiopoietin-2; IL: interleukin; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; DME: diabetic macular edema.
