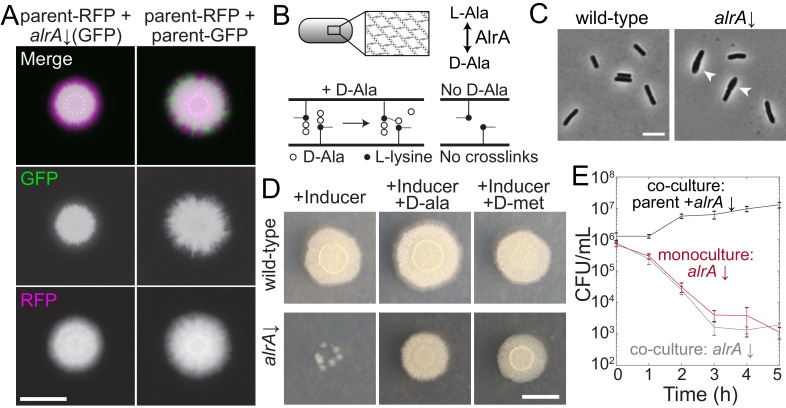
Figure 4. Full knockdown of alrA is rescued by D-alanine nutrient sharing in a biofilm colony, but not in liquid culture.
(A) Left: the sacA::gfp alrA knockdown under full knockdown was rescued by growth with the parent-RFP strain under biofilm-promoting conditions (MSgg-xylose agar). The alrA knockdown expanded beyond the boundaries of the original inoculum (dashed circle) when grown in co-culture with the parent-RFP strain. Right: the control co-culture of parent-RFP with parent-GFP preserved both strains at approximately equal proportions. Images were acquired at 24 hr. In merged images, GFP from the alrA knockdown is false-colored green and RFP from the parent-RFP strain is false-colored magenta. Scale bar: 5 mm. (B) AlrA is a racemase that converts L-alanine to D-alanine. D-alanine is critical for cell wall cross-linking. (C) Full knockdown of alrA caused cells to bulge, signifying cell wall defects. Cells were cultured for 6 hr in liquid MSgg with xylose to fully inhibit alrA expression. Arrowheads indicate bulging cells. Scale bar: 5 μm. (D) Full knockdown of alrA was rescued by exogenous D-alanine. Cultures were grown in liquid LB to an OD600 ~1 and then 1 μL was spotted on MSgg xylose agar alone or supplemented with 0.04 mg/mL D-alanine or D-methionine. Cells from alrA monocultures mostly died (left); the small colonies represent suppressors present in the initial inoculum. By contrast, addition of D-alanine (middle) or D-methionine (right) resulted in comparable growth to wild type. Images are of an unlabeled alrA knockdown (HA420) and were acquired after 24 hr of growth. Scale bar: 5 mm. (E) Full knockdown of alrA was not rescued when co-cultured with the parent-RFP strain in liquid. For the co-culture, parent and alrA knockdown cultures were mixed 1:1 and back-diluted 1:100 into liquid MSgg with xylose to fully deplete alrA. For the alrA knockdown monoculture, the culture was diluted 1:200 into liquid MSgg with xylose so that the starting inoculum of the alrA strain was equivalent to that of the co-culture. CFU/mL of the alrA knockdown were not significantly different between the monoculture (dark red) and co-culture (gray) throughout the course of the experiment (p-values from each time point range from 0.21 to 0.66, student’s unpaired t-test). The black line is the total CFU/mL of the parent/alrA knockdown co-culture. n = 3, error bars represent one standard error of the mean.