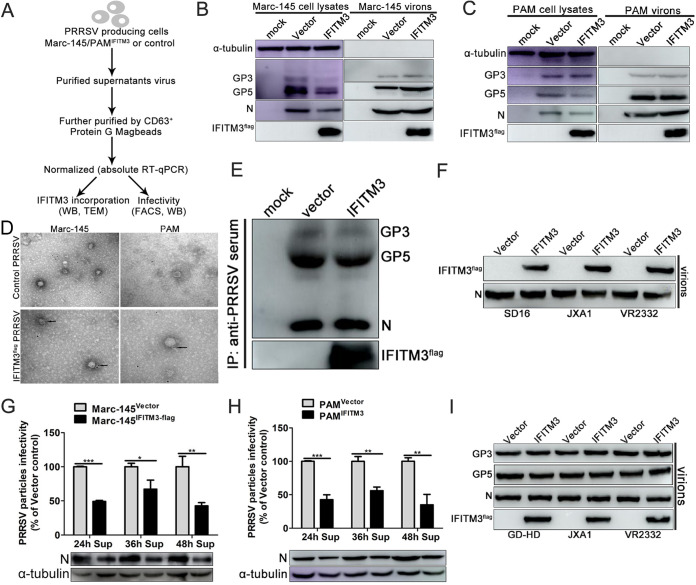
FIG 8.
IFITM3 is a PRRS virion-associated protein. (A) Representation of the experimental scheme used. (B) Marc-145-Vector or Marc-145-IFITM3-flag cells were infected with 0.1 MOI PRRSV. At 48 hpi, both cell lysates and supernatants purified by ultracentrifugation through sucrose density gradient were collected and analyzed by Western blotting. (C) As described above, PAM lysates and purified virions were analyzed. (D) Virions produced as described above were analyzed using immunogold electron microscopy. Unfixed viral preparations produced from IFITM3-overexpressing or control cells were purified and incubated with anti-flag antibodies, followed by incubation with 6 nm gold-conjugated secondary antibody. Representative pictures are presented. Scale bar, 100 nm. (E) Viral supernatants produced from IFITM3-overexpressing or control cells were concentrated and purified, followed by immunoprecipitation using swine antiserum. Western blotting was performed using an anti-flag antibody to detect IFITM3 and using swine antiserum to detect PRRSV GP3 and GP5. (F) Virions of different PRRSV strains obtained as described above were subjected to Western blotting using anti-IFITM3 antibody, and N protein was used as the loading control. (G and H) Incorporation of IFITM3 into PRRS virions decreased viral infectivity. Newly produced virions from IFITM3-overexpressing or control cells were collected 24, 36, or 48 hpi, purified, and normalized prior to infectivity analysis. (I) IFITM3 did not affect PRRSV major envelope protein processing and incorporation into viral particles. Equal amounts of N protein were loaded into each lane, and Western blotting was performed using anti-flag, swine antiserum, and anti-N antibodies. PRRSV, porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus; IFITM, interferon-induced transmembrane; MOI, multiplicity of infection; PAM, porcine alveolar macrophage; hpi, hours postinfection.