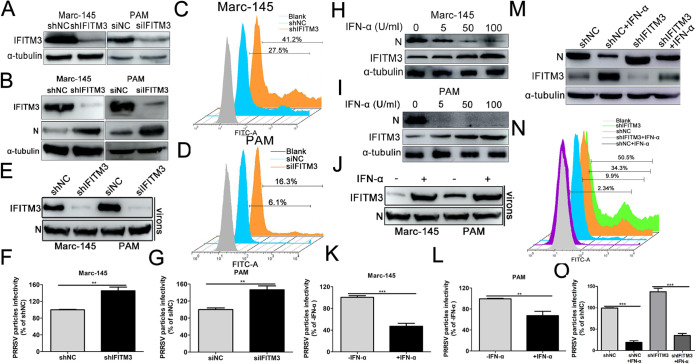
FIG 9.
Endogenous IFITM3 is incorporated into PRRSV particles and reduces the virions’ intrinsic infectivity. (A) Western blotting of endogenous IFITM3 expression in Marc-145-shIFITM3 cells or PAMs transfected with 100 nM IFITM3-specific siRNA using an anti-IFITM3 antibody. (B to D) Marc-145-shIFITM3 cells or (B and D) PAMs transfected with IFITM3 siRNA were infected with 0.1 MOI GFP-PRRSV. At 36 hpi, cells were harvested for analysis of N protein expression using Western blotting or for analysis of GFP-PRRSV-positive cells using FACS. (E to G) Marc-145-shIFITM3 cells or PAMs transfected with IFITM3-specific siRNA were challenged with GFP-PRRSV at an MOI of 0.1 at 37°C for 1 h and subsequently incubated in 3% FBS+DMEM after extensive cell washing to remove input virus. At 36 hpi, newly produced virions were collected, purified, and normalized prior to Western blotting and infectivity analysis (expressed as GFP-PRRSV positive cells). (H and I) Western blotting of PRRSV infection in Marc-145 cells or PAMs pretreated with 0, 5, 50, or 100 U/ml IFN-α for 24 h. (J to L) Marc-145 cells or PAMs were treated with 100 U/ml IFN-α and then challenged with 0.1 MOI GFP-PRRSV. Virions retrieved from infected cell supernatants were purified and normalized for IFITM3 protein or infectivity assay. (M and N) Marc-145-shNC or Marc-145-shIFITM3 cells pretreated with 100 U/ml IFN-α for 24 h were infected with GFP-PRRSV at an MOI of 0.1. Cells were collected at 36 hpi for N protein or GFP-PRRSV-positive cell analysis. (O) Virions retrieved from the supernatants shown in panel M were purified and normalized for intrinsic infectivity detection. PRRSV, porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus; IFN-α, interferon-α; IFITM, IFN-induced transmembrane; MOI, multiplicity of infection; PAM, porcine alveolar macrophage; siRNA, small interfering RNA; hpi, hours postinfection; NC, negative control.