Figure 3. Higher B7-H3 expression on solid cancers than on normal tissues, as determined by immunohistochemical and flow cytometric staining with the B7-H3-specific mAb 376.96.
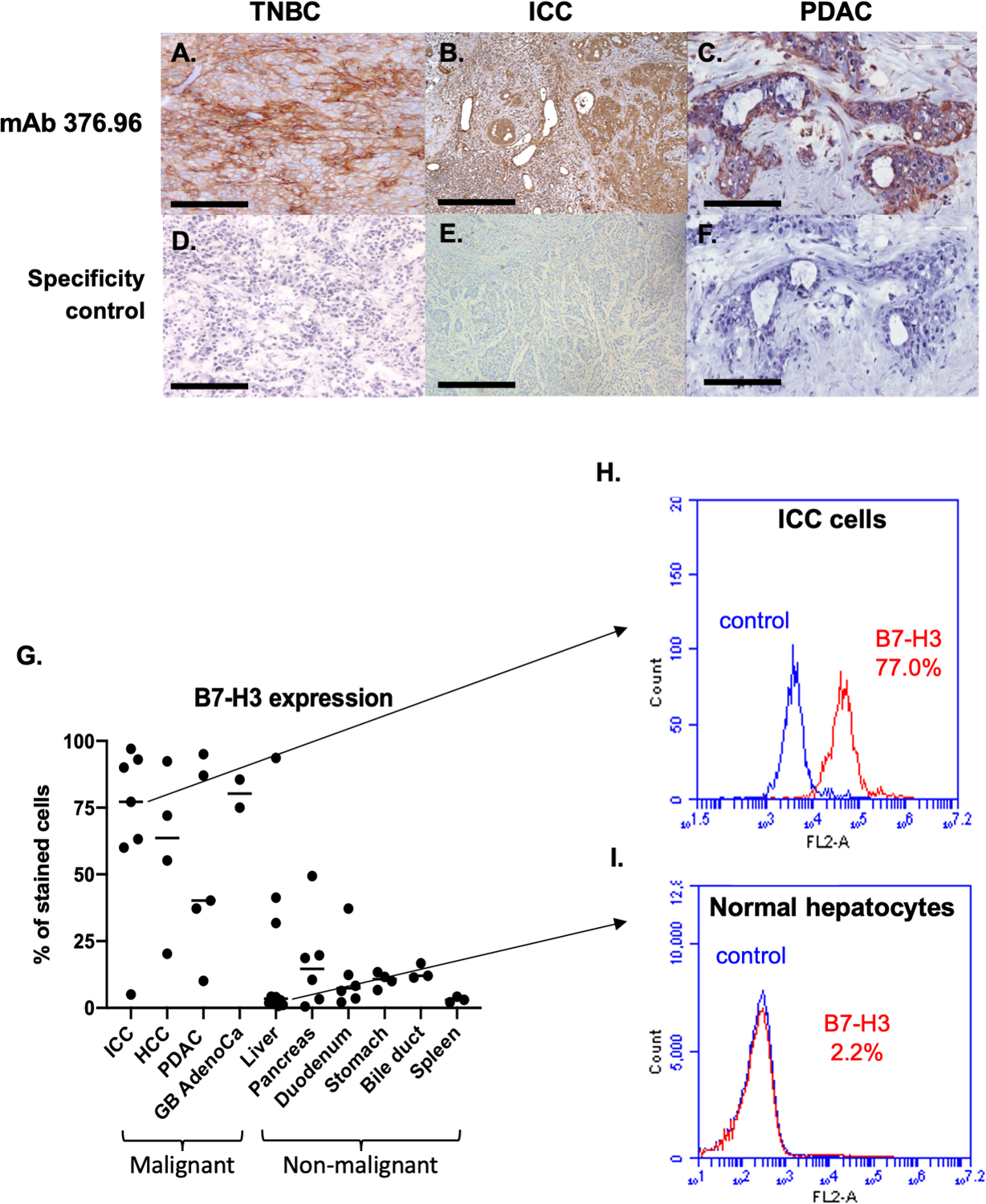
Representative micrographs of immunohistochemical staining with the B7-H3-specific mAb 376.96 of frozen tissue sections of TNBC (A), ICC (B), and PDAC (C) tumors are shown. Slides stained with the secondary antibody were used as a negative control (D, E, and F, respectively). (Magnification 200X). Surgically resected tumor specimens have a higher frequency of B7-H3-positive cells compared to normal tissues as determined by flow cytometric analysis (G). Surgically resected specimens were incubated with collagenase IV and single cell suspension was obtained. Cells were then stained with the B7-H3-specific mAb 376.96 (1ug/mL) and then analyzed by flow cytometry. Each dot on the plot represents a specimen from a different patient and the horizontal bars indicate the median value of each group. The frequency of B7-H3-positive cells was significantly higher in malignant tissues (Mann-Whitney U test, p<0.001). Of note, the liver specimen with the highest percentage of B7-H3-positive cells had underlying chronic hepatitis C, and the pancreas specimen with 50% B7-H3-positive cells had underlying chronic pancreatitis. Surgically removed ICC cells have a high frequency of B7-H3-positive cells (H), while normal liver cells adjacent to cancer tissue have a low frequency of B7-H3-positive cells (I), as determined by flow cytometric analyses. Cells were stained with the B7-H3-specific mAb 376.96 and rabbit anti-mouse IgG-PE antibodies. The isotype-matched mAb F3-C25 was used as a control for mAb 376.96. Stained cells were subjected to flow cytometry analysis. The percentage of cells stained with the B7-H3-specific mAb 376.96 are shown in each histogram. TNBC: triple negative breast cancer; ICC: intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; PDAC: pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; GB AdenoCa: gallbladder adenocarcinoma.
