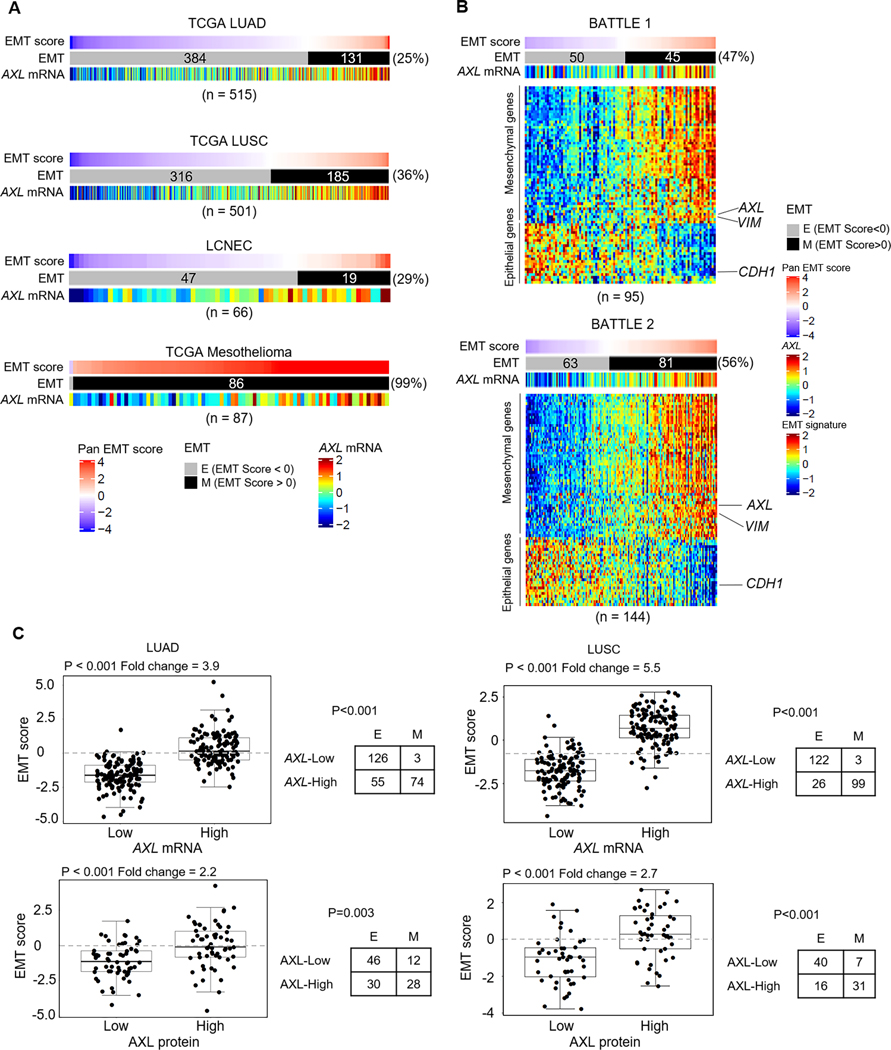
Figure 1. AXL is a potential therapeutic target in a subset of treatment-naïve and treatment-resistant lung tumors.
A. Range of EMT scores and AXL mRNA expression in treatment-naïve patient cohorts - lung adenocarcinoma (TCGA LUAD), lung squamous cell carcinoma (TCGA LUSC), large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) and mesothelioma. B. EMT scores, EMT gene signature and AXL mRNA expression in tumor samples from treatment-refractory advanced NSCLC patients, obtained post-progression (BATTLE-1, BATTLE-2). C. Using a quartile cutoff for AXL expression (mRNA (Top) and protein (Bottom)), EMT scores of LUAD and LUSC tumors with AXL-high (4th quantile) and AXL-low (1st quantile) expression were compared by Welch’s t-test. Fold change in EMT score between AXL-high and AXL-low tumors are indicated. Frequency of epithelial (E; EMT score < 0) and mesenchymal (M; EMT score > 0) tumors in the two expression groups was analyzed by Pearson’s Chi-squared test with Yates’ continuity correction.